Can Circulating MicroRNAs, Cytokines, and Adipokines Help to Differentiate Psoriatic Arthritis from Erosive Osteoarthritis of the Hand? A Case-Control Study
- PMID: 40429765
- PMCID: PMC12111288
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26104621
Can Circulating MicroRNAs, Cytokines, and Adipokines Help to Differentiate Psoriatic Arthritis from Erosive Osteoarthritis of the Hand? A Case-Control Study
Abstract
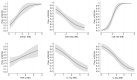
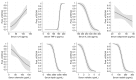
The differential diagnosis of erosive osteoarthritis of the hand (EHOA) and psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is challenging, especially considering the absence of specific diagnostic biomarkers. The aim of the present study was to evaluate whether a pattern of microRNAs (miRNAs) (miR-21, miR-140, miR-146a, miR-155, miR-181a, miR-223), pro-inflammatory cytokines [interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, IL-17a, IL-23a, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α], and adipokines (adiponectin, chemerin, leptin, resistin, and visfatin) could help to differentiate EHOA from PsA. Fifty patients with EHOA, fifty patients with PsA, and fifty healthy subjects (HS) were studied. The gene expression of miRNAs and cytokines were evaluated by real-time PCR from peripheral blood mononuclear cells and serum levels of cytokines and adipokines were quantified by ELISA in PsA and EHOA patients and HS. Gene expression showed the significant up-regulation of the analyzed miRNAs in EHOA and PsA patients as compared to HS and higher miR-155 in EHOA vs. PsA patients. The expression levels of IL-1β and IL-6 did not show any significant differences between EHOA and PsA, while IL-17a and IL-23a were significantly up-regulated in PsA compared to EHOA. Circulating TNF-α levels were higher in EHOA compared to PsA, while PsA patients exhibited significantly elevated levels of IL-23a. The combination of miR-155 with C-reactive protein enhanced the ability to differentiate EHOA from PsA, further supporting the potential of miR-155 as a diagnostic biomarker.
Keywords: adipokines; biomarkers; cytokines; erosive osteoarthritis of the hand; miR-155; microRNAs; psoriatic arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Tenti S., Ferretti F., Gusinu R., Gallo I., Giannotti S., Pozza A., Fioravanti A., Coluccia A. Impact of thumb osteoarthritis on pain, function, and quality of life: A comparative study between erosive and non-erosive hand osteoarthritis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020;39:2195–2206. doi: 10.1007/s10067-020-04982-z. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

