Biomarkers as Beacons: Illuminating Sepsis-Associated Hepato-Renal Injury
- PMID: 40429966
- PMCID: PMC12112447
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26104825
Biomarkers as Beacons: Illuminating Sepsis-Associated Hepato-Renal Injury
Abstract
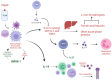
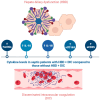
Sepsis, defined as a dysregulated host response to infection, is one of the leading causes of mortality worldwide. It unleashes in the organism a cascade of molecules, cytokines, and proteins which leads to an inflammatory storm. If this response to infection is uncontrolled, any organ is susceptible to damage. Acute kidney injury (AKI) is one of the most frequent organ dysfunctions in septic patients, and while it can be reversible, its presence leads to a higher burden of morbidity and mortality. While serum creatinine is essential in evaluating kidney function, the pathophysiology of AKI is not completely elucidated, and a plethora of novel biomarkers have been studied in the hope of an early diagnosis and fast treatment. While the liver is not as affected by sepsis, it plays an important role as a guardian by providing acute-phase proteins, activating neutrophils, and controlling iron balance. Acute liver failure (ALF) could impair the organism's capacity to contain and eliminate pathogens. Some molecules have been associated with either AKI or ALF, although biomarkers specific for organ dysfunction are difficult to validate. The aim of this review is to understand the role of several molecules in the pathophysiology of sepsis and their clinical ability for diagnosing or predicting sepsis-induced hepato-renal dysfunction.
Keywords: IL-18; IL-27; acute kidney injury; acute liver failure; ferritin; hepcidin; sepsis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sepsis-mediated renal dysfunction: Pathophysiology, biomarkers and role of phytoconstituents in its management.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Sep;165:115183. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115183. Epub 2023 Jul 22. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 37487442 Review.
-
Soluble CD25 is increased in patients with sepsis-induced acute kidney injury.Nephrology (Carlton). 2014 Jun;19(6):318-24. doi: 10.1111/nep.12230. Nephrology (Carlton). 2014. PMID: 24646167
-
Metabolomics- and proteomics-based multi-omics integration reveals early metabolite alterations in sepsis-associated acute kidney injury.BMC Med. 2025 Feb 11;23(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s12916-025-03920-7. BMC Med. 2025. PMID: 39934788 Free PMC article.
-
[Research progress on biomarkers of sepsis-associated acute kidney injury].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2024 Nov;36(11):1216-1220. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20231018-00883. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2024. PMID: 39697031 Review. Chinese.
-
Angiopoietin-2 outperforms other endothelial biomarkers associated with severe acute kidney injury in patients with severe sepsis and respiratory failure.Crit Care. 2021 Feb 4;25(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s13054-021-03474-z. Crit Care. 2021. PMID: 33541396 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Miftode R.-S., Costache I.-I., Constantinescu D., Mitu O., Timpau A.-S., Hancianu M., Leca D.-A., Miftode I.-L., Jigoranu R.-A., Oancea A.-F., et al. Syndecan-1: From a Promising Novel Cardiac Biomarker to a Surrogate Early Predictor of Kidney and Liver Injury in Patients with Acute Heart Failure. Life. 2023;13:898. doi: 10.3390/life13040898. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

