Preliminary Evaluation of Plasma circ_0009910, circ_0027478, and miR-1236-3p as Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 40429981
- PMCID: PMC12111893
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26104842
Preliminary Evaluation of Plasma circ_0009910, circ_0027478, and miR-1236-3p as Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
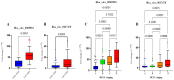
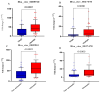
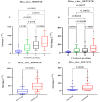
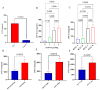
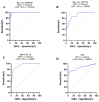
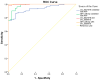
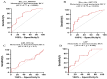
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are increasingly recognized as significant regulators in multiple cancers, such as hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), frequently affecting microRNA (miRNA) expression. The diagnostic and prognostic roles of circRNAs, specifically circ_0009910 and circ_0027478, in conjunction with miR-1236-3p, in HCC, have not yet been fully investigated. In this pilot study, we assessed the expression levels of circ_0009910, circ_0027478, and miR-1236-3p in plasma samples from 100 patients diagnosed with HCC and 50 healthy controls through reverse transcriptase-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR). The diagnostic performance was evaluated using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis, and correlations with clinicopathological features were examined. Circ_0009910 and circ_0027478 exhibited significant upregulation in patients with HCC (p < 0.05), whereas miR-1236-3p demonstrated downregulation (p < 0.05). Circ_0009910 demonstrated significant diagnostic accuracy (area under the curve [AUC] = 0.90), effectively differentiating HCC from controls and showing a correlation with tumor size, metastasis, and alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) levels (p < 0.05). Both circ_0009910 and circ_0027478 exhibited a positive correlation with clinicopathological features, whereas miR-1236-3p demonstrated an inverse correlation. Logistic regression validated the diagnostic and prognostic capabilities of these biomarkers. The results indicate that circ_0009910, circ_0027478, and miR-1236-3p, in conjunction with AFP three, present a promising diagnostic and prognostic profile for HCC. Additional validation in larger cohorts is required to establish their clinical utility.
Keywords: circRNAs; circ_0009910; circ_0027478; hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); miR-1236-3; plasma biomarkers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors disclose no conflicts of interest, including any investment, personal or other relationships with other entities or organizations that may improperly affect the work in this paper or are perceived to affect it.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Exploring a circulating circRNA and miRNA biomarker panel for early detection of ovarian cancer through multiple omics analysis.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 16;15(1):25809. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-11641-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40670591 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating miR-542-3p as a Prognostic Marker for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Cell Mol Med. 2025 Jul;29(14):e70748. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70748. J Cell Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40717227 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Novel Liver-Specific Pseudogene Biomarker, BMS1P8, for Diagnosis and Prognosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2025 Jul 29;30(7):41684. doi: 10.31083/FBL41684. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2025. PMID: 40765359
-
Hsa_circ_0088036 promotes tumorigenesis and chemotherapy resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma via the miR-140-3p/KIF2A axis.Histol Histopathol. 2025 Aug;40(8):1239-1251. doi: 10.14670/HH-18-849. Epub 2024 Nov 19. Histol Histopathol. 2025. PMID: 39587911
-
Identification of circulating MicroRNAs as novel potential biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma detection: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Transl Oncol. 2015 Sep;17(9):684-93. doi: 10.1007/s12094-015-1294-y. Epub 2015 May 9. Clin Transl Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25956842
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

