DDM1 Maintains Heterochromatin by Regulating Histone Variants
- PMID: 40429984
- PMCID: PMC12112423
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26104845
DDM1 Maintains Heterochromatin by Regulating Histone Variants
Abstract
Chromatin remodeling factors efficiently and precisely establish, maintain, regulate, and distinguish between chromatin states in eukaryotes. DECREASE in DNA METHYLATION 1 (DDM1) is an important heterochromatin remodeling factor in plants that is responsible for maintaining heterochromatin DNA methylation and suppressing most transposable elements. Previous studies have predominantly focused on the effects of DDM1 on chromatin, with only a few focusing on its remodeling mechanisms. However, recent studies have greatly advanced understanding of the remodeling functions of DDM1 and, in particular, have clarified the mechanisms involved. In this review, we discuss the newly identified remodeling functions and mechanisms of DDM1. As DDM1 is closely involved in histone variant exchange, we first introduce the main histone variants associated with chromatin states in plants. Next, we focus on how DDM1 promotes the deposition of specific histone variants and describe its other remodeling functions. We propose that the core function of DDM1 is the regulation of histone variant distribution. DDM1 maintains heterochromatin by regulating the deposition of H2A and H3 variants, particularly by facilitating the exchange of specific histone variants.
Keywords: DDM1; TE silencing; chromatin remodeling factors; heterochromatin maintenance; histone variant exchange; histone variants.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
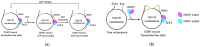


References
-
- Niu Y., Bai J., Zheng S. The Regulation and Function of Histone Methylation. J. Plant Biol. 2018;61:347–357. doi: 10.1007/s12374-018-0176-6. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2021YFD2200103/the National Key R&D Program of China during the 14th Five-year Plan Period
- 2572024DP24/the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities
- LH2024C047/Heilongjiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China
- 202410225248/Funded Projects of the Innovation and Entrepreneurship Program for 2022 Undergraduates of Northeast Forestry University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

