The Role of AP2/ERF Transcription Factors in Plant Responses to Biotic Stress
- PMID: 40430060
- PMCID: PMC12112388
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26104921
The Role of AP2/ERF Transcription Factors in Plant Responses to Biotic Stress
Abstract
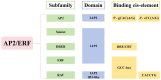
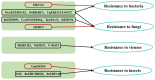
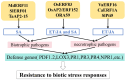
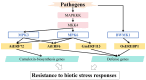
The APETALA2/ethylene response factor (AP2/ERF) family of transcription factors (TFs) is one of the largest and most important TF families in plants. This family plays a crucial role in regulating growth, development, and responses to both biotic and abiotic stresses. This study provides a comprehensive overview of the structure, classification, and distribution of AP2/ERF TFs in various plant species, with particular emphasis on their roles in responses to biotic stress. These findings provide valuable insights for future research on AP2/ERF TFs and their potential applications in crop improvement through molecular breeding.
Keywords: AP2/ERF; biotic stress; molecular breeding; regulation expression; transcription factors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
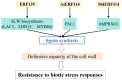
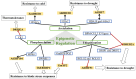
Similar articles
-
Genome-wide investigation of the AP2/ERF gene family in ginger: evolution and expression profiling during development and abiotic stresses.BMC Plant Biol. 2021 Nov 25;21(1):561. doi: 10.1186/s12870-021-03329-3. BMC Plant Biol. 2021. PMID: 34823471 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the AP2/ERF transcription factor family in Eriobotrya japonica and its role in exogenous melatonin-mediated regulation of salt stress.Funct Integr Genomics. 2025 Jul 27;25(1):161. doi: 10.1007/s10142-025-01667-1. Funct Integr Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40715545
-
Genome-wide characterization of the AP2/ERF gene family in radish (Raphanus sativus L.): Unveiling evolution and patterns in response to abiotic stresses.Gene. 2019 Nov 15;718:144048. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2019.144048. Epub 2019 Aug 14. Gene. 2019. PMID: 31421189
-
APETALA2/ethylene-responsive factors in higher plant and their roles in regulation of plant stress response.Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2024 Dec;44(8):1533-1551. doi: 10.1080/07388551.2023.2299769. Epub 2024 Jan 24. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38267262 Review.
-
Understanding AP2/ERF Transcription Factor Responses and Tolerance to Various Abiotic Stresses in Plants: A Comprehensive Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 11;25(2):893. doi: 10.3390/ijms25020893. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38255967 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sakuma Y., Liu Q., Dubouzet J.G., Abe H., Shinozaki K., Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K. DNA-binding specificity of the ERF/AP2 domain of Arabidopsis DREBs, transcription factors involved in dehydration- and cold-inducible gene expression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002;290:998–1009. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2001.6299. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AA23073001/the Science and Technology Major Project of Guangxi
- 32360247/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2023GXNSFAA026453/the Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi
- AA22036003 and AA22117002/the Science and Technology Major Project of Guangxi
- 2021YT010/the Fundamental Research Fund of Guangxi Academy of Agriculture Sciences
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

