Genome-Wide Identification of Ginkgo biloba SPL Gene Family and Expression Analysis in Flavonoid Biosynthesis and Water Stress
- PMID: 40430070
- PMCID: PMC12112263
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26104932
Genome-Wide Identification of Ginkgo biloba SPL Gene Family and Expression Analysis in Flavonoid Biosynthesis and Water Stress
Abstract
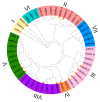
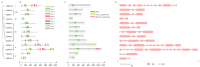
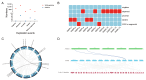
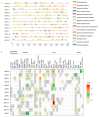
SQUAMOSA promoter-binding protein-like (SPL) transcription factors specific to plants are vital for regulating growth, development, secondary metabolite biosynthesis, and responses to both biotic and abiotic stresses. Despite their importance, no systematic investigations or identifications of the SPL gene family in Ginkgo biloba have been conducted. In this study, we identified 13 SPL genes within the Ginkgo biloba reference genome, spanning seven chromosomes, and categorized these genes into six groups based on their phylogenetic relationships with Arabidopsis thaliana SPL gene families. Our analysis of gene structure, conserved domains, motifs, and miR156 target predictions indicates that GbSPLs are highly conserved across evolutionary timelines. Furthermore, synteny analysis highlighted that dispersed duplication events have expanded the SPL gene family in Ginkgo biloba. Examination of the cis-regulatory elements revealed that many GbSPL genes possess motifs associated with light, hormones, and stress, implying their involvement in flavonoid biosynthesis and adaptation to environmental conditions. RNA-Seq and qRT-PCR expression profiles of GbSPL genes across various tissues and low- and high-flavonoid leaves and during both short-term and long-term water stress illustrated their roles in flavonoid biosynthesis and responses to water stress. Subcellular localization experiments showed that GbSPL2 and GbSPL11 proteins are situated within the nucleus. Our research offers the first systematic characterization of the SPL gene family in Ginkgo biloba, establishing a valuable foundation for understanding their evolutionary background and functional roles in flavonoid biosynthesis and water stress response.
Keywords: Ginkgo biloba; SPL; flavonoid biosynthesis; gene family; water stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of NAC family genes in Ginkgo biloba L.Plant Biol (Stuttg). 2023 Jan;25(1):107-118. doi: 10.1111/plb.13486. Epub 2022 Nov 30. Plant Biol (Stuttg). 2023. PMID: 36377299
-
An R2R3-MYB transcription factor as a negative regulator of the flavonoid biosynthesis pathway in Ginkgo biloba.Funct Integr Genomics. 2014 Mar;14(1):177-89. doi: 10.1007/s10142-013-0352-1. Epub 2013 Dec 4. Funct Integr Genomics. 2014. PMID: 24306138
-
Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the SPL gene family and its response to abiotic stress in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.).BMC Genomics. 2024 Sep 9;25(1):846. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10773-6. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39251952 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization and functional analysis of a MYB gene (GbMYBFL) related to flavonoid accumulation in Ginkgo biloba.Genes Genomics. 2018 Jan;40(1):49-61. doi: 10.1007/s13258-017-0609-5. Epub 2017 Sep 4. Genes Genomics. 2018. PMID: 29892898
-
Ginkgo biloba flavonoids: Analysis of functions, regulatory mechanisms, and extraction.Plant Biol (Stuttg). 2025 Jun 3. doi: 10.1111/plb.70054. Online ahead of print. Plant Biol (Stuttg). 2025. PMID: 40462387 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

