Physicochemical and Biological Modifications in Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Derived Conditioned Media Under Hypoxic Preconditioning: Impact on Oxidative Stress and Nanoparticle Stability
- PMID: 40430131
- PMCID: PMC12113433
- DOI: 10.3390/life15050702
Physicochemical and Biological Modifications in Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Derived Conditioned Media Under Hypoxic Preconditioning: Impact on Oxidative Stress and Nanoparticle Stability
Abstract
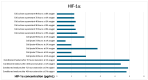
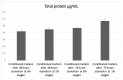
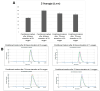
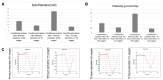
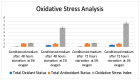
Hypoxic preconditioning (HP) is a promising approach to enhance the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) by modulating their oxidative stress response, metabolic activity, and secretome composition. Conditioned media (CM) obtained from MSCs cultured under hypoxia contains bioactive molecules and extracellular vesicles (EVs) that support regenerative processes. However, the effects of varying oxygen levels on the redox status and physicochemical characteristics of MSC-derived CM remain incompletely understood. This study aimed to investigate how two physiologically relevant oxygen concentrations (1% and 5%) influence oxidative stress parameters and nanoparticle features in Wharton's jelly-derived MSC (WJ-MSC)-conditioned media. Cells were cultured under 1% or 5% O2 and subjected to serum starvation for 48 or 72 h. CM samples were analyzed for total oxidant status (TOS), total antioxidant status (TAS), and oxidative stress index (OSI). Nanoparticle size and zeta potential were evaluated using dynamic light scattering (DLS), and HIF-1α levels were quantified via ELISA. Results showed that CM from 1% O2 cultures exhibited significantly higher oxidative stress, with elevated TOS and OSI values and reduced TAS levels, particularly after 72 h. Nanoparticle size was initially larger under 1% O2 but decreased with time, whereas 5% O2 supported more stable size profiles. Zeta potential measurements revealed more negative values under 5% O2, indicating greater colloidal stability. HIF-1α expression markedly increased under 1% O2, confirming hypoxia-induced cellular adaptation. In conclusion, this study demonstrates that graded hypoxia distinctly modulates oxidative stress and nanoparticle characteristics in MSC-derived CM. These findings provide a basis for optimizing hypoxic preconditioning protocols to improve the quality and therapeutic potential of acellular MSC-based therapies.
Keywords: HIF-1α; conditioned media; hypoxic preconditioning; mesenchymal stem cells; nanoparticle stability; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
LincRNA-p21 promotes mesenchymal stem cell migration capacity and survival through hypoxic preconditioning.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018 Oct 25;9(1):280. doi: 10.1186/s13287-018-1031-x. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 30359325 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic analysis of metabolic and ultrastructural changes in mesenchymal stem cells at hypoxic preconditioning and post-preconditioning stages: Cobalt chloride on the spotlight.Tissue Cell. 2025 Aug;95:102923. doi: 10.1016/j.tice.2025.102923. Epub 2025 Apr 19. Tissue Cell. 2025. PMID: 40267849
-
Hypoxia Conditioned Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Induce Increased Vascular Tube Formation in vitro.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2019 Oct 23;7:292. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2019.00292. eCollection 2019. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31709251 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-Conditioned Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Tissue Regeneration Application.Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2022 Oct;28(5):966-977. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEB.2021.0145. Epub 2022 Jan 10. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2022. PMID: 34569290 Review.
-
Innovative preconditioning strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of extracellular vesicles derived from mesenchymal stem cells in gastrointestinal diseases.Inflammopharmacology. 2023 Dec;31(6):2973-2993. doi: 10.1007/s10787-023-01350-6. Epub 2023 Oct 24. Inflammopharmacology. 2023. PMID: 37874430 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pulido-Escribano V., Torrecillas-Baena B., Camacho-Cardenosa M., Dorado G., Gálvez-Moreno M.Á., Casado-Díaz A. Role of Hypoxia Preconditioning in Therapeutic Potential of Mesenchymal Stem-Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles. World J. Stem Cells. 2022;14:453. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i7.453. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

