Fixation Stability of the Right and Left Eyes Under Binocular and Monocular Viewing Conditions
- PMID: 40430132
- PMCID: PMC12112839
- DOI: 10.3390/life15050703
Fixation Stability of the Right and Left Eyes Under Binocular and Monocular Viewing Conditions
Abstract
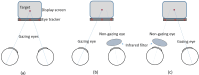
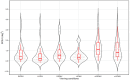
Herein, we investigated changes in fixation stability between the right and left eyes during binocular and monocular viewing in young adults without strabismic binocular vision disorders. Fixation stability was assessed using the bivariate contour ellipse area (BCEA) in 34 healthy participants (15 males, 19 females) in their 20s. Eye-tracking was performed under three conditions: binocular viewing, monocular viewing, and monocular occlusion. Under these conditions, the median BCEA (deg2) values for the right and left eyes were 0.95 and 0.75, 1.07 and 0.86, and 1.62 and 1.32, respectively. Fixation stability did not differ significantly between the right and left eyes under the same viewing conditions. However, the left eye demonstrated greater fixation stability under binocular viewing (closed loop/both eyes open) than the right eye under monocular viewing (open loop/one eye closed). Participants with a dominant left eye in binocular viewing had higher fixation stability than those with a dominant right eye. During monocular occlusion, the nondominant eye showed better fixation stability than the dominant eye. A significant quantitative correlation was observed between phoria and fixation stability in the left eye during binocular viewing. These findings show that fixation stability changes with different viewing conditions and is affected by which eye is covered. Therefore, when conducting tests such as ocular alignment, which involve covering one eye, it may be helpful to assess both right and left eye occlusion for ensuring a more comprehensive analysis.
Keywords: binocular viewing; bivariate contour ellipse area (BCEA); dominant eye; fixation stability; monocular viewing; phoria.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Schor C., Hallmark W. Slow control of eye position in strabismic amblyopia. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1978;17:577–581. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

