Stress-Induced Depression and Its Effects on Tooth Wear in Rats: A 3D Dental Scan Imaging Perspective
- PMID: 40430140
- PMCID: PMC12113425
- DOI: 10.3390/life15050712
Stress-Induced Depression and Its Effects on Tooth Wear in Rats: A 3D Dental Scan Imaging Perspective
Abstract
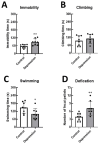
Background: In addition to behavioral and biochemical abnormalities, a parafunction associated with temporomandibular joint disorders (TMDs) resulted in stress-induced depression in rats. Exploring how chronic stress influences molar wear in rodents provides insights into the understanding of depression, TMD, and oral health. This study aimed to conduct a three-dimensional (3D) analysis of first molar wear in an animal model of depression by comparing molar attrition and cusp variation between stressed male rats and control groups.
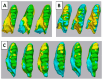
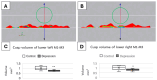
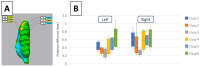
Methods: After obtaining a validated model of depression in male rats, we obtained 3D scans of lower molars to analyze wear patterns. The 3D analysis was applied to quantify cusps' volume and the difference in first molar cusp morphological structure. The data were then compared to identify significant morphological differences between groups side by side.
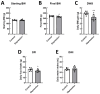
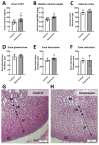
Results: The analysis revealed the reduction of cusps' volume in the depression groups. Rats exposed to depression exhibited significantly greater occlusal table wear than their control counterparts (p < 0.05).
Conclusions: As dentistry moves towards greater digital imaging, understanding the impact of psychological factors on TMD becomes increasingly necessary. This study shows that stress-induced depression in rats can result in significant tooth wear, as investigated using a 3D dental scanner.
Keywords: bruxism; dental digital scanner; depression; restraint stress; temporomandibular disorder; three-dimensional analysis; tooth wear.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Major Depression—National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) [(accessed on 5 March 2025)]; Available online: https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/statistics/major-depression.
-
- Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation Global Health Data Exchange (GHDx) [(accessed on 5 March 2025)]. Available online: https://vizhub.healthdata.org/gbd-results.
-
- Evans-Lacko S., Aguilar-Gaxiola S., Al-Hamzawi A., Alonso J., Benjet C., Bruffaerts R., Chiu W.T., Florescu S., de Girolamo G., Gureje O., et al. Socio-Economic Variations in the Mental Health Treatment Gap for People with Anxiety, Mood, and Substance Use Disorders: Results from the WHO World Mental Health (WMH) Surveys. Psychol. Med. 2018;48:1560–1571. doi: 10.1017/S0033291717003336. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

