Restoring Biomechanical Gait Function with Ultrasound-Guided Acupotomy for Post-Stroke Equinovarus Foot: Two Case Reports and a Protocol (A CARE- and SPIRIT-Compliant Study)
- PMID: 40430192
- PMCID: PMC12113240
- DOI: 10.3390/life15050766
Restoring Biomechanical Gait Function with Ultrasound-Guided Acupotomy for Post-Stroke Equinovarus Foot: Two Case Reports and a Protocol (A CARE- and SPIRIT-Compliant Study)
Abstract
Background: Post-stroke equinovarus foot (EVF) impairs gait stability, increases the risk of secondary injuries, and contributes to elevated healthcare costs. However, effective targeted interventions for EVF remain limited.
Patient concerns: Two patients with chronic EVF-a 63.5-year-old male (9.7 months post-stroke) and a 35.7-year-old female (24.5 months post-stroke)-presented with ankle deformity, gait asymmetry, and impaired balance, all of which interfered with daily activities.
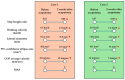
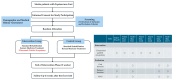
Intervention and outcomes: Both patients underwent ultrasound-guided acupotomy targeting spastic ankle muscles, administered over four sessions within two weeks. A quantitative gait analysis revealed substantial improvements in step length ratios (Case 1: 0.61 → 0.86; Case 2: 0.67 → 0.88), as well as enhancements in walking velocity, lateral symmetry, postural balance, and Modified Ashworth Scale scores. No adverse events were reported. Protocol proposal: Based on these observations, a prospective randomized controlled trial is planned to compare ultrasound-guided acupotomy plus conventional therapy versus conventional therapy alone. Outcomes will be assessed quantitatively using gait analysis. Lessons and implications: Ultrasound-guided acupotomy may offer a minimally invasive, targeted approach to releasing spastic muscles while preserving neurovascular structures, thereby improving gait function in patients with post-stroke EVF.
Keywords: case report; equinovarus foot; protocol; stroke; ultrasound-guided acupotomy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Freitas M., Fonseca P., Alves L., Pinho L., Silva S., Figueira V., Félix J., Pinho F., Vilas-Boas J.P., Silva A. Neurobiomechanical Characterization of Feedforward Phase of Gait Initiation in Chronic Stroke: A Linear and Non-Linear Approach. Appl. Sci. 2025;15:4762. doi: 10.3390/app15094762. - DOI
-
- Spina S., Facciorusso S., Botticelli C., Intiso D., Ranieri M., Colamaria A., Fiore P., Ciritella C., Genêt F., Santamato A. Ultrasonographic Evaluation of Three Approaches for Botulinum Toxin Injection into Tibialis Posterior Muscle in Chronic Stroke Patients with Equinovarus Foot: An Observational Study. Toxins. 2021;13:829. doi: 10.3390/toxins13110829. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Han T.R., Bang M.S., Chung S.G. Rehabilitation Medicine. 6th ed. Koonja Publishing Inc.; Paju, Republic of Korea: 2019.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

