Isolation, Sphalerite Bioleaching, and Whole Genome Sequencing of Acidithiobacillus ferriphilus QBS3 from Zinc-Rich Sulfide Mine Drainage
- PMID: 40430218
- PMCID: PMC12113256
- DOI: 10.3390/life15050792
Isolation, Sphalerite Bioleaching, and Whole Genome Sequencing of Acidithiobacillus ferriphilus QBS3 from Zinc-Rich Sulfide Mine Drainage
Abstract
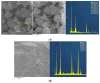
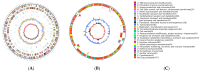
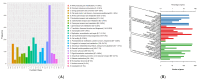
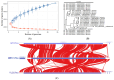
The genus Acidithiobacillus has been widely used in bioleaching, and novel strains in this genus, such as A. ferriphilus, have also been confirmed to possess bioleaching capabilities. In this study, an Acidithiobacillus ferriphilus strain, QBS3, was isolated from zinc-rich sulfide mine drainage using the gradient dilution method. QBS3 is a Gram-negative, 1.3 µm rod-shaped bacterium with small red colonies. It showed a high iron oxidation efficiency of 0.361 g/(L·h) and a sulfur oxidation efficiency of 0.206 g/(L·d). QBS3 has sphalerite bioleaching ability; using QBS3 for pure sphalerite bioleaching, 18.8% of zinc was extracted in 14 days at 1% pulp density. Whole genome sequencing was performed on QBS3. Functional prediction showed that 9.13% of the genes were involved in replication, recombination, and repair. Bioleaching-related genes were analyzed, including iron and sulfur oxidation genes, and carbon and nitrogen fixation genes. For iron oxidation, the Cyc2→RusA pathway and Iro→RusB pathway were found in QBS3. In terms of sulfur oxidation, QBS3 has an incomplete SOX system and lacks the SDO gene, but Rho and Trx may complement the SOX system, enabling QBS3 to oxidize sulfur. QBS3 has multiple sets of carbon fixation genes, and nitrogen fixation genes were also identified. A hypothetical sphalerite bioleaching model is proposed; this study provides a theoretical basis for the zinc sulfide ore bioleaching industry.
Keywords: Acidithiobacillus ferriphilus; bioleaching; ferrous oxidation; isolation; sphalerite; sulfur oxidation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures








References
-
- Shi S., Fang Z., Ni J. Comparative study on the bioleaching of zinc sulphides. Process Biochem. 2006;41:438–446. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2005.07.008. - DOI
-
- Ubaldini S., Veglió F., Toro L., Abbruzzese C. Biooxidation of arsenopyrite to improve gold cyanidation: Study of some parameters and comparison with grinding. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1997;52:65–80. doi: 10.1016/S0301-7516(97)00041-0. - DOI
-
- Zou G., Papirio S., Lai X., Wu Z., Zou L., Puhakka J., Ruan R. Column leaching of low-grade sulfide ore from Zijinshan copper mine. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2015;139:11–16. doi: 10.1016/j.minpro.2015.04.005. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

