Antimicrobial, Antioxidant, and α-Glucosidase-Inhibitory Activities of Prenylated p-Hydroxybenzoic Acid Derivatives from Oberonia ensiformis
- PMID: 40430304
- PMCID: PMC12114510
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules30102132
Antimicrobial, Antioxidant, and α-Glucosidase-Inhibitory Activities of Prenylated p-Hydroxybenzoic Acid Derivatives from Oberonia ensiformis
Abstract
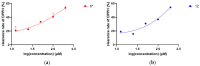
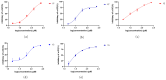
Seven previously undescribed prenylated p-hydroxybenzoic acid derivatives, oberoniaensiformisins A-G, were isolated from an EtOH extract of the whole plant Oberonia ensiformis. Their structures were determined through spectroscopic analyses (IR, NMR) and HRESIMS analysis. The isolated compounds were tested for their antimicrobial, antioxidant, and α-glucosidase-inhibitory activity. Among them, compounds 6 and 12 exhibited potential antioxidant activity, while compounds 5, 6, 12, 13, and 15 showed varying degrees of α-glucosidase-inhibitory activity, with IC50 values ranging from 34.03 to 106.10 μg/mL.
Keywords: Oberonia ensiformis; antioxidant activity; prenylated aromatic compounds; α-glucosidase-inhibitory activity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Identification of highly potent α-glucosidase inhibitory and antioxidant constituents from Zizyphus rugosa bark: enzyme kinetic and molecular docking studies with active metabolites.Pharm Biol. 2017 Dec;55(1):1436-1441. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2017.1304426. Pharm Biol. 2017. PMID: 28320255 Free PMC article.
-
A new phenolic acid from the wood of Mangifera gedebe.Nat Prod Res. 2021 Aug;35(15):2579-2582. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2019.1680666. Epub 2019 Oct 23. Nat Prod Res. 2021. PMID: 31642695
-
Phenolic compounds, antioxidant and α-glucosidase inhibitory activities from moringa oleifera seed by-products.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 2;15(1):22878. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-06916-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40596503 Free PMC article.
-
α-Glucosidase inhibition by prenylated and lavandulyl compounds from Sophora flavescens roots and in silico analysis.Int J Biol Macromol. 2017 Sep;102:960-969. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.04.092. Epub 2017 Apr 26. Int J Biol Macromol. 2017. PMID: 28455256
-
A new biflavonoid and a new triterpene from the leaves of Garcinia paucinervis and their biological activities.J Nat Med. 2017 Oct;71(4):642-649. doi: 10.1007/s11418-017-1092-7. Epub 2017 May 26. J Nat Med. 2017. PMID: 28550652
References
-
- Chase M.W., Cameron K.M., Freudenstein J.V., Pridgeon A.M., Salazar G., van den Berg C., Schuiteman A. An updated classification of Orchidaceae. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2015;177:151–174. doi: 10.1111/boj.12234. - DOI
-
- State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine . Zhong Hua Ben Cao [Chinese Materia Medica] Shanghai Science and Technology Press; Shanghai, China: 1999.
-
- National Pharmacopoeia Commission . Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China. 2020 ed. China Medical Science Press; Beijing, China: 2020.
-
- Ren F.C., Liu L., Lv Y.F., Bai X., Kang Q.J., Hu X.J., Zhuang H.D., Yang L., Hu J.M., Zhou J. Antibacterial Prenylated p-Hydroxybenzoic Acid Derivatives from Oberonia myosurus and Identification of Putative Prenyltransferases. J. Nat. Prod. 2021;84:417–426. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.0c01101. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jong T.-T., Chau S.-W. Antioxidative activities of constituents isolated from Pandanus odoratissimus. Phytochemistry. 1998;49:2145–2148. doi: 10.1016/S0031-9422(98)00390-2. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

