AMPEC4: Naja ashei Venom-Derived Peptide as a Stimulator of Fibroblast Migration with Antibacterial Activity
- PMID: 40430339
- PMCID: PMC12114029
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules30102167
AMPEC4: Naja ashei Venom-Derived Peptide as a Stimulator of Fibroblast Migration with Antibacterial Activity
Abstract
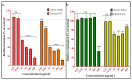
The treatment of proctological conditions, including hemorrhoids, anal fissures, and perianal abscesses, is often complicated by bacterial infections, particularly those involving multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli. This study presents the synthesis, characterization, and biological evaluation of the newly designed synthetic peptide AMPEC4, inspired by cytotoxin 5 from Naja ashei snake venom. AMPEC4 demonstrated potent antimicrobial properties with MIC values of 100 and 200 µg/mL, effectively inhibiting biofilm formation (up to 84%) and eradicating the pre-formed biofilm by up to 35%. The antibacterial activity of AMPEC4 was further supported by a membrane permeabilization assay, demonstrating its capacity to disrupt bacterial membrane integrity in a dose-dependent manner. Furthermore, AMPEC4 significantly promoted fibroblast migration, a critical step in tissue regeneration, while exhibiting notable biocompatibility, as evidenced by the absence of hemolytic, cytotoxic, and genotoxic effects. By addressing both infection control and tissue regeneration, AMPEC4 represents a promising therapeutic strategy for managing chronic wounds, particularly in the challenging environment of the anorectal region. Its ability to target Escherichia coli reference and clinical strains while accelerating the wound-healing process underscores its potential for future clinical applications.
Keywords: Escherichia coli; Naja ashei; antibiofilm activity; antimicrobial peptide; fibroblasts; proctology; wound healing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures








References
-
- Almeida J.R., Mendes B., Lancellotti M., Franchi G.C., Passos Ó., Ramos M.J., Fernandes P.A., Alves C., Vale N., Gomes P., et al. Lessons from a Single Amino Acid Substitution: Anticancer and Antibacterial Properties of Two Phospholipase A2-Derived Peptides. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022;44:46–62. doi: 10.3390/cimb44010004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

