Protective Role of Whey Protein Isolate on MPP+-Induced Differentiation of SH-SY5Y Cells by Modulating the Nrf2 Antioxidant Pathway
- PMID: 40430379
- PMCID: PMC12114080
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules30102207
Protective Role of Whey Protein Isolate on MPP+-Induced Differentiation of SH-SY5Y Cells by Modulating the Nrf2 Antioxidant Pathway
Abstract
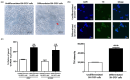
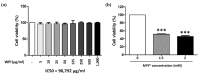
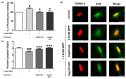
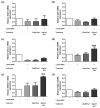
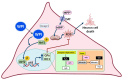
The pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease (PD) consists of the apoptosis of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc) due to oxidative stress. The present study aimed to evaluate the potential antioxidant activity of whey protein isolate (WPI) in PD models, using neurotoxin-exposed SH-SY5Y cells differentiated into dopaminergic-like neurons. Our research shows that WPI's high glutamic acid, aspartic acid, and leucine contribute to its antioxidant and neuroprotective effects, with glutamic acid crucial for glutathione synthesis. In vitro studies found that WPI, at concentrations of 5-1000 µg/mL, is non-toxic to differentiated SH-SY5Y cells. Notably, the lowest con-centration of WPI (5 µg/mL) significantly decreased intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels in these cells following a 24 h co-treatment with 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP+). The antioxidant effects of WPI were also confirmed by the increased expression of HO1 and GPx antioxidant enzymes, which are Nrf2 pathway target genes and were evaluated by real-time PCR. Furthermore, Nrf2 nuclear translocation in the differentiated SH-SY5Y cells was also increased when the cells were exposed to 5 µg/mL of WPI with MPP+. These results together suggest that WPI has antioxidant effects on dopaminergic-like neurons in a Parkinson's disease model.
Keywords: MPP+; Nrf2; Parkinson’s disease; antioxidant; whey protein isolate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Neuroprotective Role of Insulin Against MPP(+) -Induced Parkinson's Disease in Differentiated SH-SY5Y Cells.J Cell Biochem. 2016 Apr;117(4):917-26. doi: 10.1002/jcb.25376. Epub 2015 Sep 30. J Cell Biochem. 2016. PMID: 26364587
-
Neuroprotection of Andrographolide against Neurotoxin MPP+-Induced Apoptosis in SH-SY5Y Cells via Activating Mitophagy, Autophagy, and Antioxidant Activities.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 10;24(10):8528. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108528. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37239873 Free PMC article.
-
Pinostrobin Exerts Neuroprotective Actions in Neurotoxin-Induced Parkinson's Disease Models through Nrf2 Induction.J Agric Food Chem. 2018 Aug 8;66(31):8307-8318. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b02607. Epub 2018 Jul 26. J Agric Food Chem. 2018. PMID: 29961319
-
Simvastatin Protects Dopaminergic Neurons Against MPP+-Induced Oxidative Stress and Regulates the Endogenous Anti-Oxidant System Through ERK.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;51(4):1957-1968. doi: 10.1159/000495720. Epub 2018 Dec 4. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30513525
-
Rutin Attenuates Oxidative Stress Via PHB2-Mediated Mitophagy in MPP+-Induced SH-SY5Y Cells.Neurotox Res. 2023 Jun;41(3):242-255. doi: 10.1007/s12640-023-00636-5. Epub 2023 Feb 4. Neurotox Res. 2023. PMID: 36738374
References
-
- Afzal S., Manap A.S.A., Attiq A., Albokhadaim I., Kandeel M., Alhojaily S.M. From Imbalance to Impairment: The Central Role of Reactive Oxygen Species in Oxidative Stress-Induced Disorders and Therapeutic Exploration. Front. Pharmacol. 2023;14:1269581. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1269581. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

