Specialized Pro-Resolving Lipid Mediators in Pulmonary Diseases: Molecular and Therapeutic Implications
- PMID: 40430385
- PMCID: PMC12114278
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules30102212
Specialized Pro-Resolving Lipid Mediators in Pulmonary Diseases: Molecular and Therapeutic Implications
Abstract
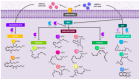
Inflammatory lung diseases (ILDs) represent a global public health crisis characterized by escalating prevalence, significant morbidity, and substantial mortality. In response to the complex immunopathogenic mechanisms driving these conditions, novel pharmacological strategies targeting resolution pathways have emerged throughout the discovery of specialized pro-resolving lipid mediator (SPM; resolvins, maresins, and protectins) dysregulation across the ILD spectra, positioning these endogenous molecules as promising therapeutic candidates for modulating maladaptive inflammation and promoting tissue repair. Over the past decade, this paradigm has catalyzed extensive translational research into SPM-based interventions as precision therapeutics for respiratory inflammation. In asthma, they reduce mucus hypersecretion, bronchial hyperreactivity, and airway inflammation, with prenatal SPM exposure potentially lowering offspring disease risk. In COPD, SPMs attenuate amyloid A-driven inflammation, normalizing cytokine/chemokine imbalances and oxidative stress and mitigating COVID-19-associated cytokine storm, enhancing survival. This review synthesizes SPMs' pharmacotherapeutic mechanisms in ILDs and evaluates current preclinical and clinical evidence.
Keywords: COPD; PUFAs; inflammation; pulmonary diseases; specialized pro-resolving lipid mediators.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Asthma. [(accessed on 18 March 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/asthma.
-
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) [(accessed on 18 March 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/chronic-obstructive-pul...
-
- COVID-19 Cases | WHO COVID-19 Dashboard. [(accessed on 1 July 2024)]. Available online: https://data.who.int/dashboards/covid19/cases.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

