Efficiently Degrading RhB Using Bimetallic Co3O4/ZnO Oxides: Ultra-Fast and Persistent Activation of Permonosulfate
- PMID: 40430410
- PMCID: PMC12114238
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules30102237
Efficiently Degrading RhB Using Bimetallic Co3O4/ZnO Oxides: Ultra-Fast and Persistent Activation of Permonosulfate
Abstract
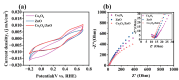
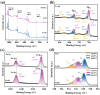
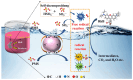
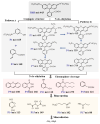
To address the issues of poor Co2+ regeneration and limited interfacial electron transfer in heterogeneous catalytic systems, this study proposes the synthesis of highly efficient and stable Co3O4/ZnO composites through the pyrolysis-oxidation reaction of Co/Zn MOFs for the degradation of rhodamine B (RhB) using activated peroxymonosulfate (PMS). The results confirmed that the catalyst exhibited a high electron transfer capacity, and the synergistic effect between the bimetals enhanced the reversible redox cycle of Co3+/Co2+. Under optimal conditions, complete removal of RhB was achieved in just 6 min using the Co3O4/ZnO composite, which demonstrated excellent stability after five cycles. Furthermore, the catalyst exhibited a high degradation efficiency in real water samples with a total organic carbon (TOC) removal rate of approximately 65% after 60 min. The electrochemical measurements, identification of active species, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analysis revealed that non-radicals (1O2 and direct charge transfer) played a major role in the degradation of RhB. Finally, the potential mechanisms and degradation pathways for RhB degradation using this catalyst were systematically investigated. This study opens new avenues for the development of efficient and stable PMS catalysts, and provides insights into the preparation of other emerging metal oxides.
Keywords: Co3O4/ZnO composite; RhB degradation; bimetallic synergy; persulfate activation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Yang Q., Zhang Y., Liang J., Luo Y., Liu Q., Yang Y., Sun X. Facile hydrothermal synthesis of co-glycerate as an efficient peroxymonosulfate activator for rhodamine B degradation. Colloid Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022;648:129239. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022.129239. - DOI
-
- Li M., Liu C., Zhang Z., Cao S., Liu H., Shen S., Wang W. Ultrathin Cu-Fe oxide nanosheets boosting persulfate activation to remove organic pollutants with coupling and transformation between radical and nonradical mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022;281:119978. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2021.119978. - DOI
-
- Pang L., Wang Y., Jia X., Yang Y., Li J., Liu H. Acetic acid mediated fabrication of highly exposed Fe(III)/Fe(II) sites in Fe2O3/MA for enhanced peroxymonosulfate activation. J. Alloys Compd. 2023;960:170649. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2023.170649. - DOI
-
- Ghanbari F., Moradi M. Application of peroxymonosulfate and its activation methods for degradation of environmental organic pollutants: Review. Chem. Eng. J. 2017;310:41–62. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.10.064. - DOI
Grants and funding
- 2022jyxm276, 2022jyxm296/the 2022 Provincial Quality Engineering Project for Higher Education Institutions of Anhui Province
- AHJZNX-2024-04/the Open Project Program of Engineering Research Center of Building Energy Efficiency Control and Evaluation, Ministry of Education under Grant
- 2304001/the Open Project Program of Anhui Institute of Urban-Rural Green Development and Urban Renewal
- STY-2024-06/the Open Project Program of Anhui Institute of Strategic Study on Carbon Dioxide Emissions Peak and Carbon Neutrality in Urban-Rural Development
- JZ202129,JZ202134/the first batch of natural science projects supported by surplus funds in 2021 of Anhui Jianzhu University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

