3,3'-((3-Hydroxyphenyl)azanediyl)dipropionic Acid Derivatives as a Promising Scaffold Against Drug-Resistant Pathogens and Chemotherapy-Resistant Cancer
- PMID: 40430804
- PMCID: PMC12115217
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens14050484
3,3'-((3-Hydroxyphenyl)azanediyl)dipropionic Acid Derivatives as a Promising Scaffold Against Drug-Resistant Pathogens and Chemotherapy-Resistant Cancer
Abstract
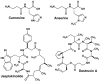
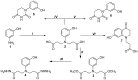
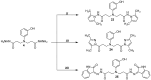
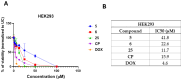
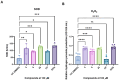
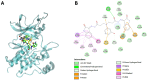
The synthesis and antimicrobial and anticancer activity of 3,3'-((3-hydroxyphenyl)azanediyl)dipropionic acid derivatives (2-25) against drug-resistant bacterial pathogens and FaDu head and neck cancer cells were investigated. The derivatives were synthesized through various methods, including esterification, hydrazinolysis, and condensation reactions. The compounds demonstrated structure-dependent antimicrobial activity, predominantly targeting Gram-positive pathogens. Compounds containing 4-nitrophenyl, 1-naphthyl, and 5-nitro-2-thienyl groups exhibited enhanced activity against S. aureus and E. faecalis. Additionally, compounds 5, 6, and 25 showed antiproliferative activity in cisplatin-resistant FaDu cells at low micromolar concentrations. The in silico modeling revealed that compound 25 interacts with the HER-2 and c-MET proteins. These compounds also induced significant oxidative stress in FaDu cells and demonstrated low cytotoxic activity in non-cancerous HEK293 cells. These results highlight the potential of N-aryl-substituted β-amino acid derivatives as promising scaffolds for the further development of novel amino acid-based antimicrobial and anticancer agents targeting drug-resistant pathogens and cancers.
Keywords: 3,3′-((3-hydroxyphenyl)azanediyl)dipropionic acid; HER2; antimicrobial activity; c-MET; head and neck cancer; multidrug-resistant pathogens; β-amino acids derivatives.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

