Biosimilars Targeting Pathogens: A Comprehensive Review of Their Role in Bacterial, Fungal, Parasitic, and Viral Infections
- PMID: 40430873
- PMCID: PMC12115129
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17050581
Biosimilars Targeting Pathogens: A Comprehensive Review of Their Role in Bacterial, Fungal, Parasitic, and Viral Infections
Abstract
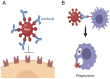
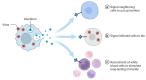
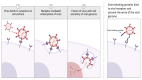
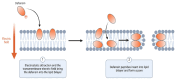
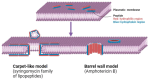
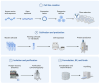
Biosimilars represent medicinal products that exhibit a high degree of similarity to an already sanctioned reference biologic agent, with negligible clinically significant disparities concerning safety, purity, or potency. These therapeutic modalities are formulated as economically viable substitutes for established biologics, thereby facilitating increased accessibility to sophisticated treatments for a range of medical conditions, including infectious diseases caused by bacterial, fungal, and viral pathogens. The current landscape of biosimilars includes therapeutic proteins, such as monoclonal antibodies, antimicrobial peptides, antiviral peptides, and antifungal peptides. Here, we discuss the obstacles inherent in the development of biosimilars, including the rapid mutation rates of pathogens. Furthermore, we discuss innovative technologies within the domain, including antibody engineering, synthetic biology, and cell-free protein synthesis, which exhibit potential for improving the potency and production efficiency of biosimilars. We end with a prospective outlook to highlight the importance and capacity of biosimilars to tackle emerging infectious diseases, highlighting the imperative need for ongoing research and financial commitment.
Keywords: antibacterial biosimilars; antifungal biosimilars; antimicrobial peptides; antiviral biosimilars; infection management; monoclonal antibodies; therapeutic proteins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Jana M.K., Chiang M.-H. Microbes of Medical Importance. Volume 3. IIP Series; Mumbai, India: 2024. Monoclonal antibodies: A promising weapon against the silent pandemic of multidrug resistant bacteria; pp. 546–568.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

