Nifuroxazide and 4-Hydroxybenzhydrazone Derivatives as New Antiparasitic (Trypanosoma cruzi and Leishmania mexicana) and Anti- Mycobacterium tuberculosis Agents
- PMID: 40430911
- PMCID: PMC12114619
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17050621
Nifuroxazide and 4-Hydroxybenzhydrazone Derivatives as New Antiparasitic (Trypanosoma cruzi and Leishmania mexicana) and Anti- Mycobacterium tuberculosis Agents
Abstract
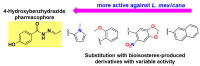
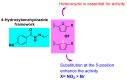
Background/Objectives: Nifuroxazide (Nfz) is a drug that has been used as a scaffold for designing antimicrobial and antiparasitic agents. This study aimed to synthesize and evaluate in vitro of Nfz and twenty-five 4-hydroxybenzhydrazone derivatives as potential anti-Trypanosoma cruzi, anti-Leishmania mexicana, and anti-Mycobacterium tuberculosis agents. Methods: The compounds were synthesized by condensing 4-hydroxybenzhydrazide with appropriate aldehydes in acidic conditions and structurally confirmed by spectroscopic techniques. All compounds were evaluated in vitro against T. cruzi strains (NINOA and A1), L. mexicana (M379 and FCQEPS strains), and M. tuberculosis (H37Rv strain), followed by enzymatic assays against T. cruzi cysteine proteases. Results: Compound Nfz-24 (IC50 = 6.8 μM) had better trypanocidal activity than the reference drugs benznidazole (IC50 > 30 μM) and nifurtimox (IC50 > 7 μM) against the NINOA strain, and Nfz-8 (IC50 = 7.2 μM) was the compound most active against the A1 strain with a high inhibition of T. cruzi cysteine proteases (IC50 = 4.6 μM) and low cytotoxic effects (CC50 >100 μM). On the other hand, compound Nfz-5 (IC50 = 5.2 μM) had a 25-fold better leishmanicidal effect than glucantime (IC50 > 125 μM) against the L. mexicana M379 strain, and compound Nfz-13 had the best leishmanicidal effects (IC50 = 10.2 μM) against the FCQEPS strain. Finally, Nfz, Nfz-1, and Nfz-2 had minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values of 12.3, 5.1, and 18.8 μg/mL against M. tuberculosis, respectively. Conclusions: In summary, these results suggest that the compounds Nfz-1, Nfz-2, Nfz-5, Nfz-8, Nfz-10, Nfz-15, Nfz-24, and Nfz-25 are candidates for further studies to develop new and more potent anti-T. cruzi, anti-leishmaniasis, and anti-M. tuberculosis agents.
Keywords: Leishmania mexicana; Trypanosoma cruzi; anti-Mycobacterium tuberculosis; cysteine protease inhibitors; hydrazone moiety; nifuroxazide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Antiparasitic Effect of Polyphenols and Terpenes from Natural Products Against Trypanosoma cruzi and Leishmania mexicana.Metabolites. 2025 Aug 21;15(8):560. doi: 10.3390/metabo15080560. Metabolites. 2025. PMID: 40863176 Free PMC article.
-
Design, Synthesis, and In Vitro and In Silico Evaluation of 1,3,4-Oxadiazoles as Anti-Trypanosoma cruzi and Anti-Leishmania mexicana Agents.ChemMedChem. 2024 Dec 2;19(23):e202400241. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.202400241. Epub 2024 Oct 23. ChemMedChem. 2024. PMID: 39136604
-
Novel prenyloxy chalcones as potential leishmanicidal and trypanocidal agents: Design, synthesis and evaluation.Eur J Med Chem. 2019 Apr 1;167:402-413. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.02.028. Epub 2019 Feb 12. Eur J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30784876
-
Germacranolide-type sesquiterpene lactones from Smallanthus sonchifolius with promising activity against Leishmania mexicana and Trypanosoma cruzi.Parasit Vectors. 2017 Nov 13;10(1):567. doi: 10.1186/s13071-017-2509-6. Parasit Vectors. 2017. PMID: 29132413 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of Antiprotozoal 2-(4-Alkyloxyphenyl)-Imidazolines and Imidazoles and Their Evaluation on Leishmania mexicana and Trypanosoma cruzi.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 26;25(7):3673. doi: 10.3390/ijms25073673. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612484 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Antiparasitic Effect of Polyphenols and Terpenes from Natural Products Against Trypanosoma cruzi and Leishmania mexicana.Metabolites. 2025 Aug 21;15(8):560. doi: 10.3390/metabo15080560. Metabolites. 2025. PMID: 40863176 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brune K. Chemistry and Pharmacology of Nitrofurans. J. Med. Chem. 2022;65:530–542.
-
- Gupta K., Hooton T.M., Naber K.G. Antimicrobial Use for Urinary Tract Infections: The Role of Nitrofurantoin. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017;64:952–960.
-
- Sok D., Hwang Y.J., Yoon J. Safety and Efficacy of Nitrofurantoin in Clinical Practice. Therapeut. Clin. Risk Manag. 2020;16:509–517.
-
- Nicolas M., McEwan G., Brown J. Advances in Nitrofurans and Their Therapeutic Potential. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2021;19:481–493.
-
- Roquini V., Mengarda A.C., Cajas R.A., Martins-da-Silva M.F., Godoy-Silva J., Santos G.A., Espírito-Santo M.C.C., Pavani T.F., Melo V.A., Salvadori M.C., et al. The Existing Drug Nifuroxazide as an Antischistosomal Agent: In Vitro, In Vivo, and In Silico Studies of Macromolecular Targets. Microbiol. Spectrum. 2023;11:e01393-23. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01393-23. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

