Large-Scale Rice Mutant Establishment and High-Throughput Mutant Manipulation Help Advance Rice Functional Genomics
- PMID: 40431057
- PMCID: PMC12114927
- DOI: 10.3390/plants14101492
Large-Scale Rice Mutant Establishment and High-Throughput Mutant Manipulation Help Advance Rice Functional Genomics
Abstract
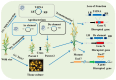
Rice (Oryza sativa L.) is a stable food for over half of the world population, contributing 50-80% of the daily calorie intake. The completion of rice genome sequencing marks a significant milestone in understanding functional genomics, yet the systematic identification of gene functions remains a bottleneck for rice improvement. Large-scale mutant libraries in which the functions of genes are lost or gained (e.g., through chemical/physical treatments, T-DNA, transposons, RNAi, CRISPR/Cas9) have proven to be powerful tools for the systematic linking of genotypes to phenotypes. So far, using different mutagenesis approaches, a million mutant lines have been established and about 5-10% of the predicted rice gene functions have been identified due to the high demands of labor and low-throughput utilization. DNA-barcoding-based large-scale mutagenesis offers unprecedented precision and scalability in functional genomics. This review summarizes large-scale loss-of-function and gain-of-function mutant library development approaches and emphasizes the integration of DNA barcoding for pooled analysis. Unique DNA barcodes can be tagged to transposons/retrotransposons, DNA constructs, miRNA/siRNA, gRNA, and cDNA, allowing for pooling analysis and the assignment of functions to genes that cause phenotype alterations. In addition, the integration of high-throughput phenotyping and OMICS technologies can accelerate the identification of gene functions.
Keywords: gain-of-function; loss-of-function; mutagenesis; mutant library and DNA barcoding; rice (Oryza sativa L.).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effort and contribution of T-DNA Insertion mutant library for rice functional genomics research in China: review and perspective.J Integr Plant Biol. 2012 Dec;54(12):953-66. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-7909.2012.01171.x. Epub 2012 Nov 29. J Integr Plant Biol. 2012. PMID: 23020748 Review.
-
Genetic resources offer efficient tools for rice functional genomics research.Plant Cell Environ. 2016 May;39(5):998-1013. doi: 10.1111/pce.12632. Epub 2015 Nov 24. Plant Cell Environ. 2016. PMID: 26301381 Review.
-
CAFRI-Rice: CRISPR applicable functional redundancy inspector to accelerate functional genomics in rice.Plant J. 2020 Oct;104(2):532-545. doi: 10.1111/tpj.14926. Epub 2020 Aug 31. Plant J. 2020. PMID: 32652789
-
Mutant resources for the functional analysis of the rice genome.Mol Plant. 2013 May;6(3):596-604. doi: 10.1093/mp/sss142. Epub 2012 Nov 30. Mol Plant. 2013. PMID: 23204502 Review.
-
High-throughput analysis of rice genes by means of the heterologous full-length cDNA overexpressor (FOX)-hunting system.Int J Dev Biol. 2013;57(6-8):517-23. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.130176mm. Int J Dev Biol. 2013. PMID: 24166434 Review.
References
-
- Hernández-Soto A., Echeverría-Beirute F., Abdelnour-Esquivel A., Valdez-Melara M., Boch J., Gatica-Arias A. Rice breeding in the new era: Comparison of useful agronomic traits. Curr. Plant Biol. 2021;27:100211. doi: 10.1016/j.cpb.2021.100211. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

