Probiotic Potential of Pediococcus pentosaceus M6 Isolated from Equines and Its Alleviating Effect on DSS-Induced Colitis in Mice
- PMID: 40431130
- PMCID: PMC12114451
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms13050957
Probiotic Potential of Pediococcus pentosaceus M6 Isolated from Equines and Its Alleviating Effect on DSS-Induced Colitis in Mice
Abstract
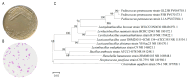
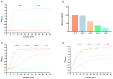
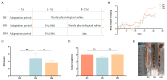
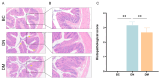
Colitis in equines has high morbidity and mortality rates, which severely affects the development of the equine-breeding industry. With the issuance of antibiotic bans, there is an urgent need for healthier and more effective alternatives. In recent years, probiotics have been widely used as microbial feed additives in animal husbandry, playing a crucial role in preventing and treating diarrhea and regulating host immune function. In this study, we isolated and screened a strain with rapid and stable acid production using bromocresol purple, litmus milk coloration tests, and acid production performance assessments. Based on morphological characteristics, physiological and biochemical properties, and 16S rDNA identification, the strain was identified as Pediococcus pentosaceus and named M6. The Pediococcus pentosaceus M6 exhibited stable growth and tolerance to high temperatures, acid and bile salt concentrations, and simulated gastrointestinal fluid environments. The M6 strain demonstrated good antibacterial effects against Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, and Salmonella. The M6 strain did not produce hemolysis zones on Columbia blood agar plates, indicating its high safety, and was found to be insensitive to 12 antibiotics, including cephalexin and neomycin. Additionally, intervention in mice with dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis alleviated weight loss and shortened colon length. To a certain extent, it regulated the expression of inflammatory cytokines and the gut microbiota within the body and reduced inflammatory cell infiltration and intestinal barrier damage. In summary, the isolated Pediococcus pentosaceus M6 strain exhibited excellent probiotic properties and could alleviate DSS-induced colitis in mice, suggesting its potential application value as a probiotic in animal husbandry.
Keywords: 16S rDNA; Pediococcus pentosaceus; equine; inflammatory bowel disease; intestinal contents.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pediococcus pentosaceus CECT 8330 protects DSS-induced colitis and regulates the intestinal microbiota and immune responses in mice.J Transl Med. 2022 Jan 15;20(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s12967-022-03235-8. J Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35033121 Free PMC article.
-
Probiotic characteristics and whole genome sequencing of Pediococcus pentosaceus SNF15 and its protective effect on mice diarrhea induced by Escherichia coli K99.Front Vet Sci. 2025 Mar 13;12:1524658. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1524658. eCollection 2025. Front Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40151573 Free PMC article.
-
New strain of Pediococcus pentosaceus alleviates ethanol-induced liver injury by modulating the gut microbiota and short-chain fatty acid metabolism.World J Gastroenterol. 2020 Oct 28;26(40):6224-6240. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i40.6224. World J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 33177795 Free PMC article.
-
Pediococcus pentosaceus, a future additive or probiotic candidate.Microb Cell Fact. 2021 Feb 16;20(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s12934-021-01537-y. Microb Cell Fact. 2021. PMID: 33593360 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pediococcus pentosaceus: Screening and Application as Probiotics in Food Processing.Front Microbiol. 2021 Dec 16;12:762467. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.762467. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34975787 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Isolation, identification and comparative genomic analysis of Lactobacillus salivarius from Mongolian horse vagina.Front Microbiol. 2025 Jul 31;16:1635639. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1635639. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40822386 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Qian S., Zhang X., Zheng X., Li R., Hao X., Tang Z., Yang Z., Sun A., Guo S., Song Y., et al. Development of interleukin-27 recombinant Lactococcus lactis and its efficacy in treating psoriasis and colitis in mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024;30:137113. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.137113. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
- 31860636/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2023YFDZ0002/Key Research and Development Project of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region
- KC2024032S/Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region Graduate Student Research Innovation Program
- BR221018, BR251007/Special Project for Capacity Building of Scientific Research Innovation Platforms under the Basic Scientific Research Fund for Directly Affiliated Universities of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

