Combination of Exhaust Gas Fermentation Effluent and Dairy Wastewater for Microalgae Production: Effect on Growth and FAME Composition of Chlorella sorokiniana
- PMID: 40431134
- PMCID: PMC12114567
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms13050961
Combination of Exhaust Gas Fermentation Effluent and Dairy Wastewater for Microalgae Production: Effect on Growth and FAME Composition of Chlorella sorokiniana
Abstract
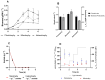
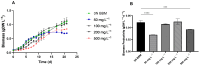
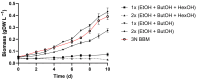
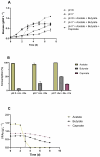
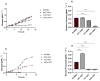
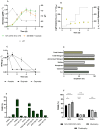
Microalgae cultivation in wastewater is a promising strategy for reducing nutrient loads and generating biomass that can be further exploited. Although microalgae grown under such conditions are not suitable for high-value applications, the resulting biomass can still be valuable for uses such as biofuels, biofertilizers, or animal feed. In this study, Chlorella sorokiniana was cultivated in dairy wastewater and, to the best of our knowledge, for the first time in a spent effluent from gas fermentation, to assess its potential as a sustainable growth medium. Growth kinetics and biomass productivity were evaluated at different dilution ratios, and it was found that high concentrations of ammonium and hexanol in undiluted effluents were inhibitory, while an optimized 50:50 dilution led to the highest biomass accumulation (1.96 g L-1) and productivity (0.5 g L-1 d-1) of C. sorokiniana. This strategy significantly reduced the nitrogen (100%), phosphate (100%), sulfate (68%), and carbon (61%) contents, demonstrating effective bioremediation activity. Furthermore, the fatty acid profile revealed an increased polyunsaturated fatty acid fraction, enhancing the potential of C. sorokiniana biomass as a feed supplement. Overall, contributing to the circular bioeconomy, this approach is scalable and cost-effective, reducing freshwater and chemical dependency in microalgae biomass production.
Keywords: FAME; dairy; gas fermentation; lipids; microalgae; mixotrophy; wastewater.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phycoremediation of dairy industry wastewater using Chlorella sorokiniana: a cost-effective strategy for biodiesel production.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2025 Jun;32(29):17407-17424. doi: 10.1007/s11356-025-36488-z. Epub 2025 May 13. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2025. PMID: 40358841
-
Lipid and biodiesel production by cultivation isolated strain Chlorella sorokiniana pa.91 and Chlorella vulgaris in dairy wastewater treatment plant effluents.J Environ Health Sci Eng. 2020 May 14;18(2):573-585. doi: 10.1007/s40201-020-00483-y. eCollection 2020 Dec. J Environ Health Sci Eng. 2020. PMID: 33312584 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Chlorella vulgaris and Chlorella sorokiniana pa.91 in post treatment of dairy wastewater treatment plant effluents.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019 Oct;26(28):29473-29489. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-06051-8. Epub 2019 Aug 8. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31396874
-
Microalgae-based livestock wastewater treatment (MbWT) as a circular bioeconomy approach: Enhancement of biomass productivity, pollutant removal and high-value compound production.J Environ Manage. 2022 Apr 15;308:114612. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.114612. Epub 2022 Feb 8. J Environ Manage. 2022. PMID: 35149401 Review.
-
Resource recovery through bioremediation of wastewaters and waste carbon by microalgae: a circular bioeconomy approach.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2021 Nov;28(42):58837-58856. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-11645-8. Epub 2021 Feb 1. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2021. PMID: 33527238 Review.
References
-
- Sadvakasova A.K., Kossalbayev B.D., Bauenova M.O., Balouch H., Leong Y.K., Zayadan B.K., Huang Z., Alharby H.F., Tomo T., Chang J.S., et al. Microalgae as a key tool in achieving carbon neutrality for bioproduct production. Algal Res. 2023;72:103096. doi: 10.1016/j.algal.2023.103096. - DOI
-
- Velea S., Oancea F., Fischer F. In: 2—Heterotrophic and Mixotrophic Microalgae Cultivation. Gonzalez-Fernandez C., Muñoz B., editors. Woodhead Publishing; Sawston, UK: 2017. pp. 45–65. (Woodhead Publishing Series in Energy).
-
- Shan S., Manyakhin A.Y., Wang C., Ge B., Han J., Zhang X., Zhou C., Yan X., Ruan R., Cheng P. Mixotrophy, a more promising culture mode: Multi-faceted elaboration of carbon and energy metabolism mechanisms to optimize microalgae culture. Bioresour. Technol. 2023;386:129512. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2023.129512. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

