Optimization of Mapping Tools and Investigation of Ribosomal RNA Influence for Data-Driven Gene Expression Analysis in Complex Microbiomes
- PMID: 40431168
- PMCID: PMC12113988
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms13050995
Optimization of Mapping Tools and Investigation of Ribosomal RNA Influence for Data-Driven Gene Expression Analysis in Complex Microbiomes
Abstract
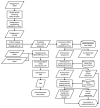
For gene expression analysis in complex microbiomes, utilizing both metagenomic and metatranscriptomic reads from the same sample enables advanced functional analysis. Due to their diversity, metagenomic contigs are often used as reference sequences instead of complete genomes. However, studies optimizing mapping strategies for both read types remain limited. In addition, although transcripts per million (TPM) is commonly used for normalization, few studies have evaluated the influence of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) in metatranscriptomic reads. This study compared Burrows-Wheeler Aligner-Maximal Exact Match (BWA-MEM) and Bowtie2 as mapping tools for metagenomic contigs. Even after optimizing Bowtie2 parameters, BWA-MEM showed higher efficiency in mapping both metagenomic and metatranscriptomic reads. Further analysis revealed that rRNA sequences contaminate predicted protein-coding regions in metagenomic contigs. When comparing TPM values across samples, contamination by rRNA led to an overestimation of TPM changes. This effect was more pronounced when the difference in rRNA content between samples was larger. These findings suggest that metatranscriptomic reads mapped to rRNA should be excluded before TPM calculations. This study highlights key factors influencing read mapping and quantification in gene expression analysis of complex microbiomes. The findings provide insights for improving analytical accuracy and advancing functional studies using both metagenomic and metatranscriptomic data.
Keywords: NGS; gene expression; metagenomics; metatranscriptomics; read mapping; ribosomal RNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Aligner optimization increases accuracy and decreases compute times in multi-species sequence data.Microb Genom. 2017 Jul 8;3(9):e000122. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000122. eCollection 2017 Sep. Microb Genom. 2017. PMID: 29114401 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of assembly algorithms for improving rate of metatranscriptomic functional annotation.Microbiome. 2014 Oct 28;2:39. doi: 10.1186/2049-2618-2-39. eCollection 2014. Microbiome. 2014. PMID: 25411636 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of variant calling tools for large plant genome re-sequencing.BMC Bioinformatics. 2020 Aug 17;21(1):360. doi: 10.1186/s12859-020-03704-1. BMC Bioinformatics. 2020. PMID: 32807073 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics tools for quantitative and functional metagenome and metatranscriptome data analysis in microbes.Brief Bioinform. 2018 Nov 27;19(6):1415-1429. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbx051. Brief Bioinform. 2018. PMID: 28481971 Review.
-
Application of computational approaches to analyze metagenomic data.J Microbiol. 2021 Mar;59(3):233-241. doi: 10.1007/s12275-021-0632-8. Epub 2021 Feb 10. J Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33565054 Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

