A Decade of Pediatric CA-MRSA Surveillance in Northern Taiwan: Retrospective Resistance Analysis and Recent Genotypic Characterization
- PMID: 40431186
- PMCID: PMC12114221
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms13051013
A Decade of Pediatric CA-MRSA Surveillance in Northern Taiwan: Retrospective Resistance Analysis and Recent Genotypic Characterization
Abstract
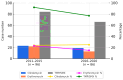
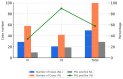
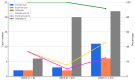
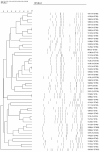
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a major cause of pediatric infections and has shown evolving molecular characteristics over time. This study aimed to investigate the phenotypic and genotypic features of MRSA isolates collected from pediatric patients at a tertiary medical center in northern Taiwan between 2011 and 2020. A total of 182 MRSA strains were analyzed for SCCmec types, PVL gene presence, antimicrobial susceptibility, multilocus sequence typing (MLST), and clonal relatedness using pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE). ST59/SCCmec Vt was the most prevalent genotype, followed by ST59/SCCmec IV and ST8/SCCmec IV. Most ST59/SCCmec Vt and ST8/SCCmec IV isolates clustered genetically. Clindamycin and erythromycin resistance remained high, whereas co-trimoxazole susceptibility ranged from 76% to 100%. These findings confirm ST59 as the dominant clone and highlight the emergence of ST8 and ST45 in community-associated MRSA (CA-MRSA) infections. Oral co-trimoxazole remains the most effective empirical option, while clindamycin and erythromycin should be avoided. Continuous molecular surveillance is warranted to monitor trends and guide treatment strategies in pediatric MRSA infections.
Keywords: MRSA; SCCmec; children; clindamycin resistance; co-trimoxazole; genotyping.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genotyping of community-associated methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA) in a tertiary care centre in Mysore, South India: ST2371-SCCmec IV emerges as the major clone.Infect Genet Evol. 2015 Aug;34:230-5. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2015.05.032. Epub 2015 Jun 1. Infect Genet Evol. 2015. PMID: 26044198
-
[Infectivity-resistotype-genotype clustering of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains in the Central Blacksea Region of Turkey].Mikrobiyol Bul. 2014 Jan;48(1):14-27. Mikrobiyol Bul. 2014. PMID: 24506712 Turkish.
-
Comparison of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated in 2003 and 2008 with an emergence of multidrug resistant ST22: SCCmec IV clone in a tertiary hospital, Malaysia.J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2013 Jun;46(3):224-33. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2013.02.001. Epub 2013 Mar 21. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2013. PMID: 23523045
-
Molecular characterization and virulence gene profiling of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus associated with bloodstream infections in southern China.Front Microbiol. 2022 Oct 17;13:1008052. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1008052. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36325019 Free PMC article.
-
Community-associated meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in children in Taiwan, 2000s.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2011 Jul;38(1):2-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2011.01.011. Epub 2011 Mar 11. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2011. PMID: 21397461 Review.
Cited by
-
Development and validation of a hierarchical machine learning method using MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry for rapid SCCmec typing and PVL detection in MRSA: a multi-centre study.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2025 Dec;14(1):2525264. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2025.2525264. Epub 2025 Jul 17. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2025. PMID: 40576568 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Turner N.A., Sharma-Kuinkel B.K., Maskarinec S.A., Eichenberger E.M., Shah P.P., Carugati M., Holland T.L., Fowler V.G., Jr. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: An overview of basic and clinical research. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019;17:203–218. doi: 10.1038/s41579-018-0147-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

