Comparative Genomic Analysis of Two Vibrio harveyi Strains from Larimichthys crocea with Divergent Virulence Profiles
- PMID: 40431301
- PMCID: PMC12114485
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms13051129
Comparative Genomic Analysis of Two Vibrio harveyi Strains from Larimichthys crocea with Divergent Virulence Profiles
Abstract
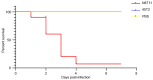
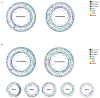
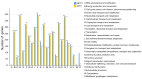
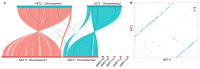
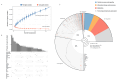
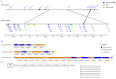
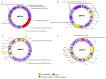
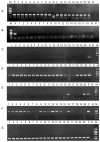
Vibrio harveyi is a significant pathogen in marine aquaculture, causing vibriosis in various marine species. This study presents a comparative genomic analysis of two V. harveyi strains, N8T11 and 45T2, which exhibit differing virulence profiles. Virulence assays revealed that N8T11 caused 92% mortality in infected fish, while 45T2 resulted in 0% mortality. Whole-genome sequencing revealed that strain N8T11 harbors five plasmids (pN8T11a, pN8T11b, pN8T11c, pN8T11d and pN8T11e) absent in 45T2, encoding genes potentially linked to virulence, such as siderophore-mediated iron acquisition and stress response mechanisms. Pan-genome analysis highlighted substantial genomic plasticity within V. harveyi, with mobile genetic elements, including plasmids and prophages, contributing to horizontal gene transfer. Conjugation experiments demonstrated that all five N8T11 plasmids can transfer to 45T2 with efficiencies up to 87%, with pN8T11b remaining stable across multiple subcultures, enabling the dissemination of virulence-associated genes. These findings suggest that plasmid-mediated gene transfer plays a role in the virulence variability observed between V. harveyi strains. This study contributes to understanding the genomic factors underlying pathogenicity in V. harveyi and provides insights for future research aimed at controlling vibriosis in aquaculture.
Keywords: Vibrio harveyi; comparative genomics; mobile genetic elements; plasmid transfer; virulence factors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Horizontal gene transfer contributes to virulence and antibiotic resistance of Vibrio harveyi 345 based on complete genome sequence analysis.BMC Genomics. 2019 Oct 22;20(1):761. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-6137-8. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31640552 Free PMC article.
-
Vibrio harveyi isolated from marine aquaculture species in eastern China and virulence to the large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea).J Appl Microbiol. 2021 Oct;131(4):1710-1721. doi: 10.1111/jam.15070. Epub 2021 Mar 20. J Appl Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33713523
-
Comparative genome analyses of five Vibrio penaeicida strains provide insights into their virulence-related factors.Microb Genom. 2022 Feb;8(2):000766. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000766. Microb Genom. 2022. PMID: 35171089 Free PMC article.
-
Vibrio harveyi: a serious pathogen of fish and invertebrates in mariculture.Mar Life Sci Technol. 2020;2(3):231-245. doi: 10.1007/s42995-020-00037-z. Epub 2020 Apr 3. Mar Life Sci Technol. 2020. PMID: 32419972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vibrio harveyi: A brief survey of general characteristics and recent epidemiological traits associated with climate change.Mar Environ Res. 2020 Feb;154:104850. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2019.104850. Epub 2019 Dec 2. Mar Environ Res. 2020. PMID: 32056705 Review.
References
-
- Ruwandeepika H.A.D., Jayaweera T.S.P., Bhowmick P.P., Karunasagar I., Bossier P., Defoirdt T. Pathogenesis, virulence factors and virulence regulation of vibrios belonging to the Harveyi clade. Rev. Aquac. 2012;4:59–74. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-5131.2012.01061.x. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

