Spatial Heterogeneity in Soil Microbial Communities Impacts Their Suitability as Bioindicators for Evaluating Productivity in Agricultural Practices
- PMID: 40431331
- PMCID: PMC12113728
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms13051160
Spatial Heterogeneity in Soil Microbial Communities Impacts Their Suitability as Bioindicators for Evaluating Productivity in Agricultural Practices
Abstract
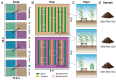
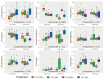
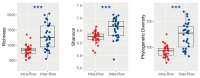
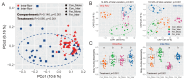
Soil microorganisms are increasingly recognized as critical regulators of farmland soil fertility and crop productivity. However, the impacts of spatial heterogeneity in soil microbial communities on bioindicators for evaluating agricultural practices remain poorly understood and warrant further validation. Through field experiments, this study investigated the differential effects of agricultural practice treatments on soil properties and bacterial communities between two main farmland soil compartments: intra-row and inter-row. Additionally, we explored the potential correlations between key taxa and soil properties, as well as maize biomass. Results revealed marked disparities in soil properties, bacterial community compositions, and co-occurrence network patterns between intra-row and inter-row soils. Agricultural practice treatments exerted significant impacts on bacterial community structures and network topological features in both intra-row and inter-row soils. Subsequent correlation analysis demonstrated strong relationships between soil properties and most keystone species. In addition, 42 and 41 indicator species were identified in intra-row and inter-row soils, respectively, including shared genera such as Solirubrobacter, Blastococcus, Iamia, Conexibacter, and Lysobacter. Notably, 22 key indicator species in intra-row soils displayed significant positive/negative correlations with maize biomass, whereas only 4 key indicator species showed negative correlations in inter-row soils. These findings highlight differential responses of bacterial communities to agricultural practices in distinct soil compartments. The intra-row soils harbored more bacterial taxa significantly associated with maize biomass, while the inter-row soils better reflected the effects of agricultural interventions. This study confirms the spatial variability of microbial communities as effective bioindicators for evaluating agricultural practice strategies. Identification of compartment-specific indicators provides novel microbiological insights into supporting precision agriculture practices.
Keywords: agricultural practices; co-occurrence network; key indicator species; soil bacterial community; spatial heterogeneity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Fertilization Alters Indicator Species Serving as Bioindicators for Evaluating Agricultural Practices Related to Maize Grain Yield.Microorganisms. 2025 Jun 13;13(6):1384. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13061384. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40572272 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial keystone taxa drive crop productivity through shifting aboveground-belowground mineral element flows.Sci Total Environ. 2022 Mar 10;811:152342. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152342. Epub 2021 Dec 15. Sci Total Environ. 2022. PMID: 34919922
-
Different types of agricultural land use drive distinct soil bacterial communities.Sci Rep. 2020 Oct 15;10(1):17418. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-74193-8. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33060673 Free PMC article.
-
Cover crop root exudates impact soil microbiome functional trajectories in agricultural soils.Microbiome. 2024 Sep 28;12(1):183. doi: 10.1186/s40168-024-01886-x. Microbiome. 2024. PMID: 39342284 Free PMC article.
-
The impacts of agroforestry interventions on agricultural productivity, ecosystem services, and human well-being in low- and middle-income countries: A systematic review.Campbell Syst Rev. 2021 Jun 1;17(2):e1167. doi: 10.1002/cl2.1167. eCollection 2021 Jun. Campbell Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 37131923 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pan H., Chen M.M., Feng H.J., Wei M., Song F.P., Lou Y.H., Cui X.M., Wang H., Zhuge Y.P. Organic and inorganic fertilizers respectively drive bacterial and fungal community compositions in a fluvo-aquic soil in northern China. Soil Till. Res. 2020;198:104540. doi: 10.1016/j.still.2019.104540. - DOI
-
- Nicolas C., Martin-Bertelsen T., Floudas D., Bentzer J., Smits M., Johansson T., Troein C., Persson P., Tunlid A. The soil organic matter decomposition mechanisms in ectomycorrhizal fungi are tuned for liberating soil organic nitrogen. ISME J. 2019;13:977–988. doi: 10.1038/s41396-018-0331-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Riggs C.E., Hobbie S.E. Mechanisms driving the soil organic matter decomposition response to nitrogen enrichment in grassland soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016;99:54–65. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2016.04.023. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

