Influence of Structured Medium- and Long-Chain Triglycerides on Muscular Recovery Following Damaging Resistance Exercise
- PMID: 40431345
- PMCID: PMC12113732
- DOI: 10.3390/nu17101604
Influence of Structured Medium- and Long-Chain Triglycerides on Muscular Recovery Following Damaging Resistance Exercise
Abstract
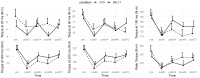
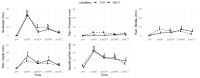
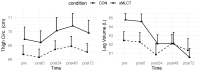
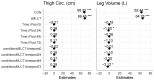
Background/Objectives: Structured medium- and long-chain triglycerides (sMLCT) may be a superior vehicle for medium-chain fatty acid delivery to peripheral tissues, such as skeletal muscle. Limited information is available concerning the effect of sMLCT on muscular performance or recovery after a muscle-damaging exercise protocol. The purpose of this study was to establish the effect of a novel formulation of sMLCT on muscular performance and recovery. Methods: Forty female adults (mean ± SD age = 22 ± 3 years; body mass index = 23.5 ± 3.4 kg/m2) were randomized into one of two study groups, placebo control [CON; n = 20] or sMLCT [n = 20], and completed five total visits to the laboratory. The baseline (i.e., pre-exercise) assessments of muscle performance, size, and soreness were compared to assessments immediately following exercise and 24, 48, and 72 h post-exercise. Results: No statistically significant condition × time interactions were noted for strength outcomes, although trends for condition × time interactions were present for torque over 25 ms (p = 0.06) and peak torque (p = 0.05). Similarly, no condition x time interactions were present for ultrasound echo intensity, the subjective ratings of soreness and pain, thigh circumference, leg volume, and vertical jump performance. Conclusions: Within the context of the current study, the ingestion of sMLCT did not significantly influence the rate of muscle strength recovery following muscle damaging resistance exercise.
Keywords: delayed onset muscle soreness; medium-chain triglycerides; muscle damage; recovery; supplements; triglycerides.
Conflict of interest statement
G.M.T. has received support for his research laboratory through funding or in-kind gifts from nutrition and sports nutrition companies. G.M.T. is the owner of Tinsley Consulting LLC, which provides paid consulting services to dietary supplement manufacturers. Bunge Loders Croklaan, the sponsor of the present study, is not a past or current client of Tinsley Consulting LLC. J.A.M. has received support for his research laboratory through funding or in-kind gifts from neuromuscular and/or occupational health entities. All the other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Romain C., Freitas T.T., Martínez-Noguera F.J., Laurent C., Gaillet S., Chung L.H., Alcaraz P.E., Cases J. Supplementation with a Polyphenol-Rich Extract, TensLess®, Attenuates Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness and Improves Muscle Recovery from Damages After Eccentric Exercise. Phytother. Res. 2017;31:1739–1746. doi: 10.1002/ptr.5902. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

