Ergogenic Effects of Combined Caffeine Supplementation and Motivational Music on Anaerobic Performance in Female Handball Players: A Randomized Double-Blind Controlled Trial
- PMID: 40431353
- PMCID: PMC12114386
- DOI: 10.3390/nu17101613
Ergogenic Effects of Combined Caffeine Supplementation and Motivational Music on Anaerobic Performance in Female Handball Players: A Randomized Double-Blind Controlled Trial
Abstract
Listening to self-selected motivational music (SSMM) during warm-ups and caffeine (CAF) intake prior to exercise can independently enhance athletic performance among female athletes. Likewise, the potential synergistic effects of these interventions have not yet been thoroughly examined.
Objective: The purpose of the study was to assess the independent and combined effects of SSMM during warm-up and pre-exercise CAF intake on maximal short-duration performance in female athletes.
Methods: Seventeen female handball players (aged 16.7 ± 0.4 years) participated in a randomized, double-blind, crossover study. Each athlete completed four conditions: (i) placebo (PLA) with no interventions, (ii) music and placebo (MUS), (iii) caffeine intake only (CAF), and (iv) a combination of music and caffeine (MUS + CAF). Performance assessments included the countermovement jump (CMJ), modified agility t-test (MAT), repeated-sprint ability (RSA) test (mean and peak sprint performance), and rating of perceived exertion (RPE).
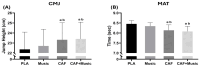
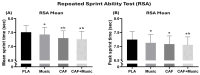
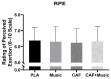
Results: The MUS (p > 0.05; p < 0.01; p < 0.01; p < 0.001, respectively), CAF (all p < 0.001), and MUS + CAF (all p < 0.01) conditions significantly outperformed the PLA condition in CMJ, MAT, RSA mean, and RSA peak measures. No significant differences were observed between the CAF and MUS + CAF conditions; however, the best performances were recorded during MUS + CAF. RPE scores remained consistent across conditions.
Conclusions: Warm-up routines incorporating either SSMM or a moderate dose of CAF (6 mg·kg-1) enhance anaerobic performance in female athletes. While both interventions are effective independently, CAF intake elicits a stronger effect. Although no significant difference was demonstrated for this combination, the concurrent use of SSMM and CAF appears to produce a potential effect, emerging as the most effective strategy for optimizing anaerobic performance.
Keywords: anaerobic performance; caffeine; handball; repeated-sprint ability; self-selected motivational music; warm-up.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Moscatelli F., Monda A., Messina A., Monda M., Monda V., Villano I., De Maria A., Nicola M., Marsala G., De Stefano M.I., et al. Evaluation of Orexin-A Salivary Levels and Its Correlation with Attention After Non-Invasive Brain Stimulation in Female Volleyball Players. Sports Med.-Open. 2024;10:32. doi: 10.1186/s40798-024-00698-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vyas A.J.V., Khanvilkar N.P. Role of Sports Psychology in Context to Development of Sports Performance. Int. J. Multidiscip. Res. 2024;6:21849. doi: 10.36948/ijfmr.2024.v06i03.21849. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

