Protective Effects of a Standardized Water Extract from the Stem of Ipomoea batatas L. Against High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity
- PMID: 40431382
- PMCID: PMC12113841
- DOI: 10.3390/nu17101643
Protective Effects of a Standardized Water Extract from the Stem of Ipomoea batatas L. Against High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity
Abstract
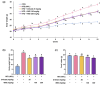
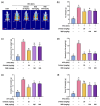
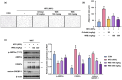
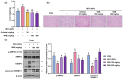
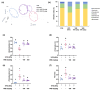
Background/Objectives: Obesity is a major health concern that can lead to various chronic diseases. Little is known about the anti-obesity effect of a standardized hot water extract from the stems of Ipomoea batatas (WIB). This study aimed to evaluate the therapeutic potential of WIB as a natural alternative to conventional anti-obesity treatments by assessing its effects on body weight, fat accumulation, and key metabolic biomarkers in a high-fat diet-induced obesity model. Methods: A high-fat diet (HFD) induced obesity in C57BL/6 mice. The mice were then treated orally with either orlistat (positive control) or WIB. Changes in body weight, food intake, and fat weight were measured, along with blood lipid profiles and adipokines. Western blot analyses were conducted to determine protein levels in each tissue. H&E staining in white adipose tissue and liver, and the gut microbiota composition were analyzed. Results: WIB treatment significantly reduced body weight and fat mass compared to the HFD group and demonstrated comparable effects to orlistat. WIB improved blood lipid profiles and adipokine levels. H&E staining revealed reduced fat accumulation in the white adipose tissue and liver. Also in those tissues, WIB restored expression levels of sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1 (SREBP-1) and CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein α (C/EBPα) and increased AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) phosphorylation. In brown adipose tissue, WIB enhanced AMPK phosphorylation and upregulated thermogenic-related proteins, including peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator-1α (PGC-1α), peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα), sirtuin 1 (SIRT1), uncoupling protein-1 (UCP-1), and cytochrome C oxidase subunit 4 (COX-IV). Analysis of gut microbiota revealed that WIB normalized β-diversity and reversed HFD-induced phyla imbalances (notably in Bacteroidetes, Firmicutes, and Proteobacteria). Conclusions: By reducing adiposity under the conditions tested in a murine model, improving metabolic markers, and favorably modulating gut microbiota, WIB demonstrates potential in mitigating obesity-related risks. These findings suggest that WIB may serve as a promising natural substance for the management of obesity. Further studies are warranted to confirm its efficacy and explore the potential underlying mechanisms in overweight or obese humans as a health supplement to help manage or prevent obesity.
Keywords: AMP-activated protein kinase; Ipomoea batatas L.; anti-obesity; brown adipose tissue; lipogenesis; liver; microbiota; thermogenesis; white-adipose tissue.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors Ye Seul Yoon and Mi-ju Kim were employed by the Dalim Biotech Co., Ltd. Authors Young-Seo Yoon and Kyung-Sook Chung were employed by the BELABEL BIO. Inc. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The authors declare that this study received funding from DALIM BIOTECH Corporation. The funder was not involved in the study design, collection, analysis, interpretation of data, the writing of this article or the decision to submit it for publication.
Figures
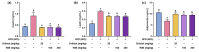

References
-
- Blackstone R.P., Blackstone R.P. Obesity-related diseases and syndromes: Insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes mellitus, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, cardiovascular disease, and metabolic syndrome. Obes. Med. Pract. Essent. Guide. 2016:83–108.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

