Nutraceutical Strategies for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD): A Path to Liver Health
- PMID: 40431398
- PMCID: PMC12113997
- DOI: 10.3390/nu17101657
Nutraceutical Strategies for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD): A Path to Liver Health
Abstract
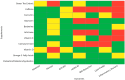
MASLD (Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease) is a growing global concern. Nutraceuticals offer an appealing approach by targeting key mechanisms, such as oxidative stress, inflammation, lipid metabolism, and insulin resistance. This narrative review examines the role of various nutraceuticals in MASLD treatment, including silymarin, vitamin E, omega-3, curcumin, berberine, and coenzyme Q10. Some of them show promising biochemical and metabolic changes, while others produce conflicting results due to relevant studies' design and endpoints. To bridge the gap between research and reality, we summarize the data, create an interpretation heatmap, and develop a practical supplement guide. Regardless of their potential, nutraceuticals should be viewed as add-ons to lifestyle interventions rather than standalone treatments. Future research should focus on well-designed, long-term studies to prove efficacy, dosing, and combination strategies for personalized MASLD management.
Keywords: MASH; MASLD; NAFLD; insulin resistance; metabolic dysfunction; nutraceuticals; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Tang G.Y., Xu Y., Zhang C., Wang N., Li H.B., Feng Y.B. Green Tea and Epigallocatechin Gallate (EGCG) for the Management of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Diseases (NAFLD): Insights into the Role of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Mechanism. Antioxidants. 2021;10:1076. doi: 10.3390/antiox10071076. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

