Abundance and Infestation of Mites on Bower's White-Toothed Rat (Berylmys bowersi) in Southwest China
- PMID: 40431519
- PMCID: PMC12115429
- DOI: 10.3390/vetsci12050426
Abundance and Infestation of Mites on Bower's White-Toothed Rat (Berylmys bowersi) in Southwest China
Abstract
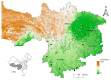
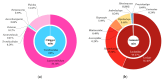
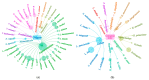
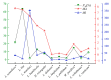
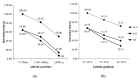
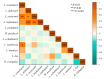
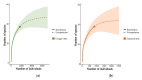
Chiggers (chigger mites) and gamasid mites are two groups of ectoparasites on rodents, and they can be the vectors or potential vectors of scrub typhus and hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS), while Bower's white-toothed rat (Berylmys bowersi) can serve as the reservoir host of the diseases. Based on field investigations at 117 survey sites of southwest China, a total of 2512 mites were collected from 55 B. bowersi rats. Under a microscope, these mites were taxonomically identified as 56 distinct species, comprising 37 chigger mite species and 19 gamasid mite species. The mite infestation burdens on B. bowersi were heavy, with a high prevalence (PM = 85.45%), mean abundance (MA = 45.67), and intensity (MI = 53.45). Of 56 mite species identified, 7 are vectors of scrub typhus and HFRS. Of the seven vector mite species, Leptotrombidium scutellare was one of dominant chigger species, with a higher infestation index on rats (PM = 21.82%, MA = 7.76) than the other six vector mite species. The sex ratio of female gamasid mites was higher than that of males. The number and infestation of adult gamasid mites were higher than those of immature mites. The infestation indexes of mites on B. bowersi hosts varied with the host's sex and age and fluctuated along different environmental gradients. The association coefficient (V) showed a slight positive association between chiggers and gamasid mites, suggesting that these two groups of mites may coexist on B. bowersi rats. Spearman correlation coefficients showed positive correlations among some dominant and vector mite species, indicating that some mite species tend to select the same hosts. A total of 69 mite species (47 chigger mite species and 22 gamasid mite species) on B. bowersi were estimated by species rarefaction and extrapolation curves. In conclusion, Berylmys bowersi has a high susceptibility to mite infestation, and it has the potential to harbor abundant mites, with heavy mite burdens. The occurrence of vector mite species, especially L. scutellare (the dominant species), increases the potential risk of transmission and the focus persistence of scrub typhus and HFRS in southwest China.
Keywords: chigger mite; gamasid mite; infestation; rodent; southwest China.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Martínez-Valdebenito C., Acosta-Jamett G., Abello R., Jiang J., Richards A.L., Abarca K., Weitzel T. Hosts and vectors of scrub typhus in Chile: Epidemiological study and molecular analyses of Orientia infection in rodents and rodent-associated mites. Parasites Vectors. 2024;17:514. doi: 10.1186/s13071-024-06602-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wang Y.C., Zhang C.T., Gao J., Chen Z.Q., Liu Z., Huang J.B., Chen Y.D., Li Z.C., Chang N., Tao Y.X., et al. Spatiotemporal trends of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS) in China under climate variation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2024;121:e2312556121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2312556121. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

