Hsa-miR-7974 Suppresses Epstein-Barr Virus Reactivation by Directly Targeting BZLF1 and BRLF1
- PMID: 40431607
- PMCID: PMC12115523
- DOI: 10.3390/v17050594
Hsa-miR-7974 Suppresses Epstein-Barr Virus Reactivation by Directly Targeting BZLF1 and BRLF1
Abstract
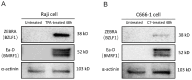
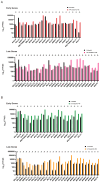
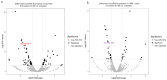
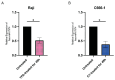
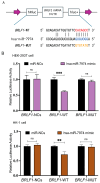
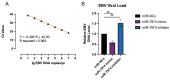
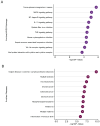
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) reactivation, a key factor in Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated malignancies, is regulated by specific cellular microRNAs (miRNAs). This study investigated the role of Hsa-miR-7974 (miR-7974) in this process. miRNA sequencing revealed significant downregulation of miR-7974 in reactivated EBV-positive cell lines (Raji and C666-1). Bioinformatics prediction and dual-luciferase assays confirmed the direct targeting of the EBV immediate-early gene BRLF1 by miR-7974. Furthermore, miR-7974 mimics suppressed, whereas inhibitors increased, the expression of key EBV lytic genes (BZLF1, BRLF1, and BMRF1) and the viral load, as validated by RT-qPCR. Bioinformatics analyses revealed the involvement of miR-7974 in cellular pathways such as membrane dynamics and signal transduction (MAPK, NF-κB, and IL-10), and its association with Hodgkin's lymphoma, leukemia, and nasopharyngeal neoplasms. These findings establish that miR-7974 functions as a crucial negative regulator of EBV reactivation by directly targeting BRLF1, highlighting its potential significance in the pathogenesis of EBV-associated malignancies.
Keywords: Epstein-Barr virus; hsa-miR-7974; lytic cycle; reactivation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Schober T., Framke T., Kreipe H., Schulz T.F., Grosshennig A., Hussein K., Baumann U., Pape L., Schubert S., Wingen A.M., et al. Characteristics of early and late PTLD development in pediatric solid organ transplant recipients. Transplantation. 2013;95:240–246. doi: 10.1097/TP.0b013e318277e344. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

