Persistent Low Anti-HIV Neutralizing Antibody Titers in HIV/HCV Coinfection Despite HCV Cure: A 5-Year Longitudinal Analysis
- PMID: 40432148
- PMCID: PMC12116166
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines13050539
Persistent Low Anti-HIV Neutralizing Antibody Titers in HIV/HCV Coinfection Despite HCV Cure: A 5-Year Longitudinal Analysis
Abstract
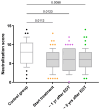
Background: Anti-HIV neutralizing antibodies (anti-HIV-nAbs) play a critical role in the immune defense against HIV by preventing viral entry and limiting replication. This study longitudinally evaluated the titers and variability of anti-HIV-nAbs in individuals coinfected with HIV and HCV. Samples were collected at three time points: before starting HCV treatment, one year after completion, and five years post-treatment. Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted on 71 HIV/HCV-coinfected patients who achieved a sustained virologic response following antiviral therapy for HCV. A control group of 41 HIV-monoinfected individuals was also included. Anti-HIV-nAb titers were evaluated by HIV neutralization assays using a panel of six recombinant HIV viruses representing multiple genetic subtypes. Generalized Linear Mixed Models and Generalized Linear Models were used for statistical analysis. p-values were adjusted using the Benjamini-Hochberg procedure (q-value). Results: HIV-neutralizing antibody responses in HIV/HCV-coinfected individuals remained stable over five years following HCV therapy without significant changes (q-value > 0.05). The mean neutralization scores remained stable, with baseline scores of 6.1 (95% CI: 5.4-6.7), 6.2 (95% CI: 5.5-6.8) at one year post-HCV therapy, and 6.0 (95% CI: 5.3-6.7) at five years post-HCV therapy. HIV/HCV-coinfected individuals consistently showed lower neutralization scores compared to the control group throughout the follow-up (q-value < 0.05). Regression analyses adjusted for age, gender, nadir CD4+, and baseline CD4+ counts confirmed that the observed differences between HIV-monoinfected and HIV/HCV-coinfected individuals persisted (q-value < 0.05) at both the baseline and after HCV therapy completion. Conclusions: Successful HCV eradication in HIV/HCV-coinfected individuals did not normalize anti-HIV-nAb titers, which remained consistently lower than those in HIV-monoinfected controls over five years.
Keywords: HCV cure; HIV; HIV neutralizing antibodies; HIV/HCV-coinfection; humoral immunity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sustained Long-Term Decline in Anti-HCV Neutralizing Antibodies in HIV/HCV-Coinfected Patients Five Years after HCV Therapy: A Retrospective Study.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Aug 30;17(9):1152. doi: 10.3390/ph17091152. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39338314 Free PMC article.
-
Negative impact of HIV infection on broad-spectrum anti-HCV neutralizing antibody titers in HCV-infected patients with advanced HCV-related cirrhosis.Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 Jun;150:113024. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113024. Epub 2022 Apr 25. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 35483197
-
Rapid decrease in titer and breadth of neutralizing anti-HCV antibodies in HIV/HCV-coinfected patients who achieved SVR.Sci Rep. 2019 Aug 21;9(1):12163. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-48592-5. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31434968 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of chronic HCV genotype 1 coinfection.Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2015 Sep;12(3):326-35. doi: 10.1007/s11904-015-0278-4. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2015. PMID: 26228050 Review.
-
A Tale of Two Viruses: Immunological Insights Into HCV/HIV Coinfection.Front Immunol. 2021 Aug 12;12:726419. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.726419. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34456931 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Platt L., Easterbrook P., Gower E., McDonald B., Sabin K., McGowan C., Yanny I., Razavi H., Vickerman P. Prevalence and burden of HCV co-infection in people living with HIV: A global systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016;16:797–808. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(15)00485-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lin W., Wang X., Zhang J., Wen C., Kang W., Mao L., Yang J., Dou Y., Shi L., Dang B., et al. A simple, feasible, efficient and safe treatment strategy of sofosbuvir/velpatasvir for chronic HCV/HIV-1 coinfected patients regardless of HCV genotypes: A multicenter, open-label study in China. Lancet Reg. Health West. Pac. 2023;36:100749. doi: 10.1016/j.lanwpc.2023.100749. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Caraballo Cortes K., Osuch S., Perlejewski K., Radkowski M., Janiak M., Berak H., Rauch A., Fehr J.S., Hoffmann M., Gunthard H.F., et al. T-Cell Exhaustion in HIV-1/Hepatitis C Virus Coinfection Is Reduced After Successful Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis C. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2023;10:ofad514. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofad514. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

