Pediatric Orthopaedic Studies Published Open Access are Associated with Increased Citation Rates
- PMID: 40432685
- PMCID: PMC12088271
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jposna.2024.100072
Pediatric Orthopaedic Studies Published Open Access are Associated with Increased Citation Rates
Abstract
Background: Open access (OA) articles are freely accessible online, either on the publisher/journal website or in a repository, a publicly available, free-of-charge online database. The primary aim of this study was to investigate whether OA publication confers a citation advantage in pediatric orthopaedics.
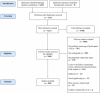
Methods: Pediatric orthopaedic studies published in English from January 1, 2012 to June 30, 2012 were identified through Excerpta medica database , Cochrane, and PubMed. Abstract screening and full-text evaluation were performed in duplicate. Citation counts over 10 years following publication, 2012 journal impact factor, OA status, type of OA, journal field, geographic location of senior author and journal publication, study design, study focus, subspecialty, level of evidence, and presence of funding were recorded. Statistical analyses were performed using independent samples t-tests, 1-way analysis of variance, χ2 tests, and multiple regression analysis.
Results: Of this study's 989 pediatric orthopaedic articles, 43.8% were OA. The mean citation count was 19.8 ± 24.4 on Web of Science. Compared to OA publications, the highest percentage of non-OA articles were published in a journal from North America, had a senior author from North America, were indexed in Journal Citation Reports, and were published in orthopaedic journals (P < .001). In multiple regression analysis, OA publication, higher levels of evidence, publication in a journal with a higher impact factor, having a senior author from Europe or North America, and study funding were associated with significantly increased citation counts. OA articles were cited an additional 3 times, on average, over 10 years.
Conclusions: Open access publication in pediatric orthopaedics confers an advantage of 3 extra citations over a decade, on average.
Key concepts: (1)Publishing pediatric orthopaedic articles open access confers an advantage of 3 additional citations over a decade compared to non-open access publication.(2)43.8% of pediatric orthopaedic articles are published open access.
Level of evidence: III.
Keywords: Citation rate; Open access; Publication trends.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Nicholas D., Watkinson A., Volentine R., Allard S., Levine K., Tenopir C., et al. Trust and authority in scholarly communications in the light of the digital transition: setting the scene for a major study. Learn Publ. 2014;27(2):121–134.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials