Use of Immune Modulating Agents to Regulate Hyperinflammation in Severe COVID 19: Assessment of Tocilizumab Use in Combination with Steroids
- PMID: 40432839
- PMCID: PMC12105767
- DOI: 10.4103/jrpp.jrpp_2_25
Use of Immune Modulating Agents to Regulate Hyperinflammation in Severe COVID 19: Assessment of Tocilizumab Use in Combination with Steroids
Abstract
Objective: In severe cases, COVID-19 can lead to a hyperinflammatory state, resulting in devastating outcomes. Immune modulation using steroids or other immune modulators can regulate the intensity of the inflammatory response; however, this theory has not been adequately assessed in practice. The current study aims to investigate the use of corticosteroids alone or in combination with tocilizumab to treat patients with severe COVID-19.
Methods: This cross-sectional study was conducted on 166 Iranian patients with severe COVID-19 infection at Al-Zahra Hospital, who were treated with the standard treatment for severe COVID-19 infection, as per the 11th version of the Iranian guideline for COVID-19 treatment. Patients were categorized into three treatment groups based on the dose of corticosteroid treatment and tocilizumab therapy: (a) high-dose methylprednisolone (>1 mg/kg) alone, (b) low-dose methylprednisolone (<1 mg/kg) followed by one dose of tocilizumab (8 mg/kg); and (c) high-dose methylprednisolone (>1 mg/kg) followed by one dose of tocilizumab (8 mg/kg). Mortality of patients as our primary outcome, laboratory parameters, length of hospitalization, intensive care unit (ICU) admission requirement, and drug-related adverse events were compared between groups.
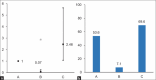
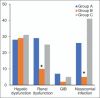
Findings: The second group showed significantly better outcomes, including shorter ICU stays, lower C-reactive protein and lactate dehydrogenase levels, and higher oxygen saturation and platelet counts than the other groups. Logistic regression revealed increased risks of mortality, nosocomial infection, and adverse effects, including hepatic and renal dysfunction and gastrointestinal bleeding, in Groups B and C compared with Group A.
Conclusion: In all evaluated parameters, a low-dose steroid followed by tocilizumab was superior to a high-dose steroid alone or combined with tocilizumab. Although this combination treatment has been assessed worldwide, few studies have focused on its application in Iranian patients with severe COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; Tocilizumab; steroids.
Copyright: © 2025 Journal of Research in Pharmacy Practice.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Multi-centre, three arm, randomized controlled trial on the use of methylprednisolone and unfractionated heparin in critically ill ventilated patients with pneumonia from SARS-CoV-2 infection: A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2020 Aug 17;21(1):724. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04645-z. Trials. 2020. PMID: 32807241 Free PMC article.
-
Intravenous methylprednisolone with or without tocilizumab in patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia requiring oxygen support: A prospective comparison.J Infect Public Health. 2021 Aug;14(8):985-989. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2021.06.003. Epub 2021 Jun 10. J Infect Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34153729 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Safety and Efficacy of Imatinib for Hospitalized Adults with COVID-19: A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2020 Oct 28;21(1):897. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04819-9. Trials. 2020. PMID: 33115543 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-6 blocking agents for treating COVID-19: a living systematic review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Mar 18;3(3):CD013881. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013881. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jun 1;6:CD013881. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013881.pub2. PMID: 33734435 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Efficacy and safety of Tocilizumab, plasmapheresis and their combination in severe COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial.Int Immunopharmacol. 2023 Feb;115:109623. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109623. Epub 2022 Dec 21. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36577157 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sadeghi S, Nasri P, Nasirian M, Mirenayat MS, Toghyani A, Khaksar M, et al. On admission hemoglobin and albumin, as the two novel factors associated with thrombosis in COVID-19 pneumonia. J Renal Inj Prev. 2022;11:31957. [doi: 10.34172/jrip.2022.31957]
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
