Potential applications of components of aged garlic extract in mitigating pro-inflammatory gene expression linked to human diseases (Review)
- PMID: 40432842
- PMCID: PMC12107228
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2025.12884
Potential applications of components of aged garlic extract in mitigating pro-inflammatory gene expression linked to human diseases (Review)
Abstract
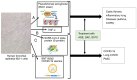
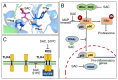
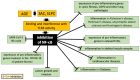
In the present review, simple approaches for the screening and characterization of natural compound agents that alter pro-inflammatory gene expression are described, with a particular focus on aged garlic extract (AGE), which has been the subject of several investigations that have supported its potential application as an anti-inflammatory agent. Additionally, evidence regarding the possible effects and mechanisms of action of two major AGE components, S-allyl cysteine (SAC) and S-1-propenyl-l-cysteine (S1PC), is reviewed. The proposed molecular targets of SAC and S1PC are IKKβ kinase, the Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1-nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 complex, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ, histone deacetylase and toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4). Targeting these molecules causes a marked reduction in NF-κB activity accompanied by a notable decrease in the transcription of NF-κB-regulated genes. Another main objective of the present review was to discuss the possibility that AGE and its bioactive components could be employed in the treatment of several human pathologies that are characterized by a hyperinflammatory state resulting from dysregulation of the TLR4 and NF-κB pathways. SAC is of interest in the treatment of lung pathologies, neurological diseases, osteoarthritis, muscular atrophy, cardiovascular diseases, diabetes and cancer. Additionally, the anti-oxidative activities of AGE, SAC and S1PC are compatible with their employment in the treatment of diseases characterized by oxidative stress, such as sickle cell disease and β-thalassemia.
Keywords: AGE; IL-8; NF-κB; TLR4; inflammation.
Copyright: © 2025 Agostinelli et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Aged Garlic Extract (AGE) and Its Constituent S-Allyl-Cysteine (SAC) Inhibit the Expression of Pro-Inflammatory Genes Induced in Bronchial Epithelial IB3-1 Cells by Exposure to the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein and the BNT162b2 Vaccine.Molecules. 2024 Dec 16;29(24):5938. doi: 10.3390/molecules29245938. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39770027 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of standardization of domestic commercial black garlic extract for S-allyl-l-cysteine and S-1-propenyl-l-cysteine.Food Sci Biotechnol. 2022 Jan 23;31(2):253-260. doi: 10.1007/s10068-021-01028-1. eCollection 2022 Feb. Food Sci Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35186355 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical and Biological Properties of S-1-Propenyl-l-Cysteine in Aged Garlic Extract.Molecules. 2017 Mar 31;22(4):570. doi: 10.3390/molecules22040570. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28362335 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic and Epigenetic Regulation of the Innate Immune Response to Gout.Immunol Invest. 2023 Apr;52(3):364-397. doi: 10.1080/08820139.2023.2168554. Epub 2023 Feb 6. Immunol Invest. 2023. PMID: 36745138 Review.
-
Sulfur-containing amino acids in aged garlic extract inhibit inflammation in human gingival epithelial cells by suppressing intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression and IL-6 secretion.Biomed Rep. 2020 Mar;12(3):99-108. doi: 10.3892/br.2019.1269. Epub 2019 Dec 30. Biomed Rep. 2020. PMID: 32042418 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Therapeutic Potential of Antioxidants in the Prevention of Human Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 19;26(12):5891. doi: 10.3390/ijms26125891. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40565368 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ohkubo S, Dalla Via L, Grancara S, Kanamori Y, García-Argáez AN, Canettieri G, Arcari P, Toninello A, Agostinelli E. The anti-oxidant, aged garlic extract, exerts cytotoxic effects on wild-type and multidrug-resistant human cancer cells by altering mitochondrial permeability. Int J Oncol. 2018;53:1257–1268. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2018.4452. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Serrano JCE, Castro-Boqué E, García-Carrasco A, Morán-Valero MI, González-Hedström D, Bermúdez-López M, Valdivielso JM, Espinel AE, Portero-Otín M. Antihypertensive effects of an optimized aged garlic extract in subjects with grade I hyper-tension and antihypertensive drug therapy: A Randomized, triple-blind controlled trial. Nutrients. 2023;15(3691) doi: 10.3390/nu15173691. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
