Label-free quantitative proteomics of gastric high-grade intraepithelial neoplasia
- PMID: 40432843
- PMCID: PMC12107227
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2025.12883
Label-free quantitative proteomics of gastric high-grade intraepithelial neoplasia
Abstract
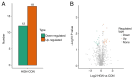
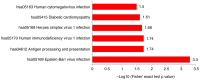
Early detection and diagnosis are key to improving the survival rate and reducing the fatality rate linked to gastric cancer. The precancerous lesion of gastric cancer is referred to as gastric high-grade intraepithelial neoplasia (HGIN). Both the sensitivity and specificity of current biomarkers that aid in the diagnosis of gastric HGIN are still relatively low. Furthermore, proteomic data on gastric HGIN are still scarce. The present study aimed to explore candidate protein biomarkers for gastric HGIN screening with proteomics and bioinformatics technology. A total of 10 serum samples were collected and categorized into two groups, i.e., the gastric HGIN and the healthy control groups. Label-free quantification in conjunction with liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry was employed to identify the probable biomarkers for gastric HGIN. Furthermore, differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) were quantified by proteomics analysis. In total, 1,192 distinct serum proteins were discovered between the gastric HGIN group and the healthy control group. DEPs were identified in the further analyses, utilizing a threshold of a 1.5-fold difference in expression level (P<0.05) in comparison with the control group. There were 18 upregulated and 12 downregulated proteins in the gastric HGIN group in comparison with the control group. Bioinformatics analyses were performed using Gene Ontology and KEGG pathway enrichment analyses. The GO analysis revealed that the DEPs were enriched in biological processes such as 'cellular', 'biological regulation', 'multicellular organismal', 'developmental' and 'reaction to stimulus processes', localized to 'cell', 'intracellular' and 'protein-containing complex', and involved in molecular functions such as 'molecular function modulator', 'binding' and 'catalytic activity'. The KEGG pathway enrichment analysis manifested that the DEPs were predominantly enriched in 'antigen processing and presentation', 'diabetic cardiomyopathy', 'Epstein-Barr virus infection', 'herpes simplex virus 1 infection', 'human immunodeficiency virus 1 infection' and 'human cytomegalovirus infection'. In conclusion, the present data provide more biological information for the formation of gastric HGIN and clues for further research on the pathogenesis of early gastric cancer.
Keywords: gastric cancer; gastric high-grade intraepithelial neoplasia; label-free; proteomics.
Copyright: © 2025 Lin et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Differential gene expression profiling of gastric intraepithelial neoplasia and early-stage adenocarcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Dec 21;20(47):17883-93. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i47.17883. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25548486 Free PMC article.
-
Whole genome expression profiling of gastric high-grade intraepithelial neoplasia with or without cancer.Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2015 Feb;37(1):23-9. doi: 10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.2015.01.005. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2015. PMID: 25676266
-
Expression of Oncostatin M in Early Gastric Cancer and Precancerous Lesions.Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2019 Dec 1;2019:3616140. doi: 10.1155/2019/3616140. eCollection 2019. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2019. PMID: 31871447 Free PMC article.
-
A Single-Center Follow-Up Study of Low-Grade Gastric Intraepithelial Neoplasia and the Screening of Key Genes of Precancerous Lesions.Front Oncol. 2022 Jun 30;12:899055. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.899055. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35847930 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting expression profiles of gastric precancerous lesions and early gastric cancer to explore crucial molecules in intestinal-type gastric cancer tumorigenesis.J Pathol. 2020 Jun;251(2):135-146. doi: 10.1002/path.5434. Epub 2020 May 27. J Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32207854 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu K, Song S, Fu T, Liu Y, Zhang H, Yan M, He Z, Zhang W, Su H, Li Z, et al. Spatiotemporal trends in the incidence of gastrointestinal neoplasms in Wuwei City of Northwestern China from 1995 to 2016: A hospital-based retrospective observational study. Front Oncol. 2021;11(712857) doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.712857. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
