Microglial dynamics and emerging therapeutic strategies in CNS homeostasis and pathology
- PMID: 40432891
- PMCID: PMC12106359
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1577809
Microglial dynamics and emerging therapeutic strategies in CNS homeostasis and pathology
Abstract
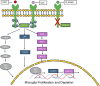
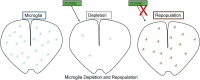
Microglia, the resident immune cells of the central nervous system (CNS), are highly dynamic and play critical roles in maintaining CNS homeostasis. Under normal conditions, microglia continuously monitor their environment, clear cellular debris, and regulate homeostasis. In response to disease or injury, however, they undergo rapid morphological and functional changes, often adopting an amoeboid shape that facilitates phagocytosis of abnormal cells, pathogens, and external antigens. Microglia also proliferate in areas of injury or pathology, contributing to immune responses and tissue remodeling. Recently, pharmacological approaches targeting microglial depletion and repopulation have gained attention as a means to reset or modulate microglial function. Techniques such as CSF1R inhibition enable transient depletion of microglia, followed by rapid repopulation, potentially restoring homeostatic functions and mitigating chronic inflammation. This review explores the current understanding of microglial dynamics and highlights emerging therapeutic applications of microglial depletion and repopulation within the CNS.
Keywords: CNS homeostasis; CSF1; CSF1R; microglia; microglia depletion; microglial dynamics; pathology; therapeutic strategies.
Copyright © 2025 Cao, Yuan, Liu, Huang and Guo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Role of Microglial Depletion Approaches in Pathological Condition of CNS.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Aug;43(6):2459-2471. doi: 10.1007/s10571-023-01326-8. Epub 2023 Feb 4. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 36738403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Restorative therapy using microglial depletion and repopulation for central nervous system injuries and diseases.Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 14;13:969127. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.969127. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35911768 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microglial depletion and repopulation in brain slice culture normalizes sensitized proinflammatory signaling.J Neuroinflammation. 2020 Jan 18;17(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s12974-019-1678-y. J Neuroinflammation. 2020. PMID: 31954398 Free PMC article.
-
CSF1R signaling is a regulator of pathogenesis in progressive MS.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Oct 23;11(10):904. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-03084-7. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 33097690 Free PMC article.
-
Established and emerging techniques for the study of microglia: visualization, depletion, and fate mapping.Front Cell Neurosci. 2024 Feb 15;18:1317125. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2024.1317125. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38425429 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Decreased IL-33 in the brain following repetitive mild traumatic brain injury contributes to cognitive impairment by inhibiting microglial phagocytosis.Mil Med Res. 2025 Aug 5;12(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s40779-025-00631-1. Mil Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40764944 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

