Ginsenoside in the treatment of type 2 diabetes and its complications: a promising traditional chinese medicine
- PMID: 40432897
- PMCID: PMC12106526
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1593780
Ginsenoside in the treatment of type 2 diabetes and its complications: a promising traditional chinese medicine
Abstract
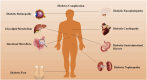
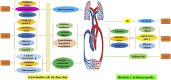
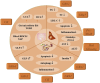
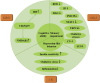
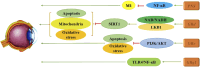
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), a chronic condition commonly observed in adults, particularly among the elderly, is characterized by a dysfunctional insulin response that impairs blood glucose regulation, resulting in persistent hyperglycemia. Ginseng, a medicinal plant with significant economic value and a longstanding history of therapeutic use in Asia, has shown efficacy against various diseases. Extensive clinical and experimental studies highlight ginsenosides, its primary bioactive compounds, for their multiple therapeutic effects across a range of conditions, including endocrine, cardiovascular, and central nervous system disorders. Various ginsenoside types have demonstrated potential in lowering blood glucose levels, reducing insulin resistance, and alleviating complications through the modulation of key protein targets and signaling pathways. This review consolidates the pharmacological actions and mechanisms of distinct ginsenosides in managing diabetes and its complications, offering a theoretical foundation for further pharmacological research and novel drug development for T2DM treatment, while also providing robust theoretical support for future clinical applications.
Keywords: complications; ginsenoside; therapeutic affect; traditional Chinese medicine; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Ju, Wang, Cui, Sun, Hu and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ginsenoside Rb1 as an Anti-Diabetic Agent and Its Underlying Mechanism Analysis.Cells. 2019 Feb 28;8(3):204. doi: 10.3390/cells8030204. Cells. 2019. PMID: 30823412 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical potential and mechanistic insights of mulberry (Morus alba L.) leaves in managing type 2 diabetes mellitus: Focusing on gut microbiota, inflammation, and metabolism.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Apr 24;306:116143. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116143. Epub 2023 Jan 9. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36632855 Review.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Ginsenosides as an Adjuvant Treatment for Diabetes.Front Pharmacol. 2018 May 1;9:423. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00423. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29765322 Free PMC article. Review.
-
UHPLC-MS-Based Serum and Urine Metabolomics Reveals the Anti-Diabetic Mechanism of Ginsenoside Re in Type 2 Diabetic Rats.Molecules. 2021 Nov 3;26(21):6657. doi: 10.3390/molecules26216657. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34771066 Free PMC article.
-
Review on ginseng and its potential active substance G-Rg2 against age-related diseases: Traditional efficacy and mechanism.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Jan 30;337(Pt 1):118781. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118781. Epub 2024 Sep 12. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39260708 Review.
References
-
- Bingbing L., Jieru L. I., Jianchao S. I., Qi C., Shengchang Y., Ensheng J. I. (2023). Ginsenoside Rb1 alleviates chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced diabetic cardiomyopathy in db/db mice by regulating the adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase/Nrf2/heme oxygenase-1 signaling pathway. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 43, 906–914. 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20221206.004 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

