TMEM132A: a novel susceptibility gene for lung adenocarcinoma combined with venous thromboembolism identified through comprehensive bioinformatic analysis
- PMID: 40432920
- PMCID: PMC12107398
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1564114
TMEM132A: a novel susceptibility gene for lung adenocarcinoma combined with venous thromboembolism identified through comprehensive bioinformatic analysis
Abstract
Background: Mounting evidence indicates that lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) patients are at elevated risk for venous thromboembolism (VTE), presenting a major clinical challenge. This study utilized public databases to identify crosstalk genes (CGs) between LUAD and VTE, applied machine learning methods to discover shared diagnostic biomarkers, and explored their underlying mechanisms.
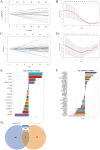
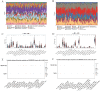
Methods: Disease-specific genes for VTE were extracted from comprehensive genomic databases (CTD, DisGeNET, GeneCards, OMIM), while transcriptomic profiles of LUAD and VTE cohorts were retrieved from GEO via GEOquery implementation. Molecular crosstalk analysis identified candidate genes through differential expression algorithms and disease-association metrics. Functional annotation employed GO and KEGG analyses to elucidate the biological significance of identified CGs. LASSO regression analysis of VTE and LUAD matrices yielded overlapping diagnostic biomarkers. Immune contexture was characterized via CIBERSORT deconvolution, followed by correlation analyses between hub genes and immune infiltration profiles. Hub genes expression was corroborated through independent cohort validation and serological quantification. Diagnostic utility was evaluated through receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve and nomogram. Therapeutic potential was assessed via DSigDB-based drug sensitivity profiling.
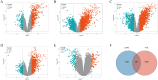
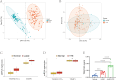
Result: Through transcriptomic analysis, we identified 381 CGs, which demonstrated significant enrichment in inflammatory cascades, immunological processes, and coagulation pathways. LASSO regression analysis of LUAD and VTE cohorts revealed TIMP1 and TMEM132A as putative shared diagnostic biomarkers. TMEM132A exhibited significant correlation with immune cell infiltration patterns across both diseases, modulating the immune microenvironment. Validation cohorts and serological assessment confirmed elevated TMEM132A expression in LUAD and LUAD combined with VTE phenotypes. The diagnostic accuracy of TMEM132A was substantiated by ROC curves and nomogram analyses. Pharmacological sensitivity analysis indicated that TMEM132A may serve as a potential target for the therapeutic agents birabresib and abemaciclib.
Conclusion: TMEM132A demonstrates diagnostic utility as a predictive biomarker for VTE occurrence in LUAD, suggesting its potential role as a susceptibility gene in this patient cohort.
Keywords: Lasso algorithm; diagnostic biomarker; immune infiltration; lung adenocarcinoma; venous thromboembolism.
Copyright © 2025 Xie, Liu, Bai, Ming, Zheng, Zhu and Qi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comprehensive bioinformatics analysis reveals the crosstalk genes and immune relationship between the systemic lupus erythematosus and venous thromboembolism.Front Immunol. 2023 Jul 3;14:1196064. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1196064. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37465678 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis to identify a novel diagnostic marker of lung adenocarcinoma and its immune infiltration landscape.Front Oncol. 2023 Jun 20;13:1199608. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1199608. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37409245 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of effective biomarkers for venous thrombosis embolism in Behçet's disease based on comprehensive bioinformatics analysis.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 10;14(1):15884. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-66973-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38987624 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of transcriptomics and radiomics revealed the potential of TEDC2 as a diagnostic marker for lung adenocarcinoma.PeerJ. 2024 Nov 14;12:e18310. doi: 10.7717/peerj.18310. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 39553728 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of cancer stemness and M2 macrophage-associated biomarkers in lung adenocarcinoma.Heliyon. 2023 Aug 16;9(9):e19114. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19114. eCollection 2023 Sep. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37662825 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

