Analysis and assessment of biomedical scientists' needs for clinical laboratory: activity-based management as an evaluation methodology
- PMID: 40433062
- PMCID: PMC12106407
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1569800
Analysis and assessment of biomedical scientists' needs for clinical laboratory: activity-based management as an evaluation methodology
Abstract
Introduction: Healthcare systems have to protect citizens' health by developing models combining concepts of efficiency, effectiveness and quality of care. The post-Covid-19 pandemic context has highlighted the relevance of efficiently managing and allocating human resources. In this scenario, the analysis and calculation of personnel needs take on strategic importance. The project aims to suggest a methodology to define the needs of Biomedical Scientists. The goal is to create a standard model adaptable to different contexts.
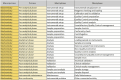
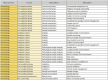
Methods: This project, developed in cooperation with the Italian Society of Clinical Biochemistry and Clinical Molecular Biology, has created a new format following the "Activity Based Management" approach. It is characterized by continuous improvements, based on analysis of processes, broken down into sub-processes and activities. After the phase of format development, a phase of application to different contexts, such as biochemistry and the hematology sectors, followed.
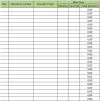
Results: The suggested methodology allows to estimate the number of Full Time Equivalents necessary for the management of the laboratory processes. Furthermore, an objective and analytical data is obtained, because it is based on timely numerical surveys that included productivity and execution times of the different activities.
Discussion: Using the format had a relevant impact on the analysis of the processes, their efficiency, and their possible improvement. This method allowed to evaluate and improve the analytical and "extra-production" activities, often underestimated but having a decisive role in the process. The proposed format can be considered a valid tool for laboratory managers to analyze and evaluating the needs of Biomedical Scientists in the laboratory. Activity Based Management allowed us to obtain precise and objective data and, at the same time, to focus on the main objective of any clinical laboratory: to create value for the patient by supporting diagnosis and treatment of paths through safe and reliable laboratory tests, which depends on a correct allocation of human resources.
Keywords: activity based management; biomedical scientist; clinical laboratory; management of healthcare organizations; staffing needs.
Copyright © 2025 Bizzoni, Napolitano, Cesa, Sacella, Bianciardi, Ottomano, Mancini and Da Rin.
Conflict of interest statement
Author LS was employed by SYNLAB Italia Srl. Author CO was employed by SYNLAB Italia Srl. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
-
Developing an efficient scheduling template of a chemotherapy treatment unit: A case study.Australas Med J. 2011;4(10):575-88. doi: 10.4066/AMJ.2011.837. Epub 2011 Oct 31. Australas Med J. 2011. PMID: 23386870 Free PMC article.
-
A research roadmap for complementary and alternative medicine - what we need to know by 2020.Forsch Komplementmed. 2014;21(2):e1-16. doi: 10.1159/000360744. Epub 2014 Mar 24. Forsch Komplementmed. 2014. PMID: 24851850
-
The Effectiveness of Integrated Care Pathways for Adults and Children in Health Care Settings: A Systematic Review.JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2009;7(3):80-129. doi: 10.11124/01938924-200907030-00001. JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2009. PMID: 27820426
-
Evidence Brief: The Effectiveness Of Mandatory Computer-Based Trainings On Government Ethics, Workplace Harassment, Or Privacy And Information Security-Related Topics [Internet].Washington (DC): Department of Veterans Affairs (US); 2014 May. Washington (DC): Department of Veterans Affairs (US); 2014 May. PMID: 27606391 Free Books & Documents. Review.
References
-
- Decreto Ministeriale 24.01 (2023). Metodo per la determinazione del fabbisogno di personale ospedaliero - AGENAS. Available online at: https://www.camera.it/temiap/2024/05/24/OCD177-7234.pdf
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

