Impact of codon optimization on vip3Aa11 gene expression and insecticidal efficacy in maize
- PMID: 40433150
- PMCID: PMC12106571
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1579465
Impact of codon optimization on vip3Aa11 gene expression and insecticidal efficacy in maize
Abstract
Introduction: Codon optimization is critical for high expression of foreign genes in heterologous systems. The vip3Aa11 gene from Bacillus thuringiensis is a promising candidate for controlling Spodoptera frugiperda.
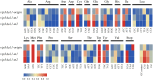
Methods and results: To develop insect-resistant maize, we designed two codon-optimized vip3Aa11 variants (vip3Aa11-m1 and vip3Aa11-m2) based on maize codon usage bias. Both recombinant proteins expressed in Escherichia coli exhibited high insecticidal activity. However, in transgenic maize, Vip3Aa11-m1 exhibited strong insecticidal activity against Spodoptera frugiperda and Spodoptera exigua, while Vip3Aa11-m2 lost activity despite identical amino acid sequences. RT-PCR analysis confirmed that both genes were transcribed correctly, but western blot results demonstrated a smaller product for vip3Aa11-m2, suggesting a translation-level alteration. Segment replacement and point mutation experiments in maize protoplasts demonstrated that the synonymous codon AAT (Asn) at the fourth amino acid position in vip3Aa11-m2 was associated with the production of a truncated protein, suggesting that the AAT codon may influence the selection of the translation initiation site, potentially shifting it to a downstream ATG (Met) codon.
Discussion: These findings not only reveal the critical role of codon context in translation initiation and protein integrity but also provide a novel strategy for optimizing foreign genes in crop improvement, particularly offering valuable insights for engineering insect-resistant maize using Bt genes.
Keywords: Spodoptera frugiperda; codon optimization; synonymous codon substitution; transgenic maize; translation initiation; vip3Aa11 gene.
Copyright © 2025 Li, Wen, Lv, Zhang, Wang and Lang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Agarwal P., Gautam T., Singh A. K., Burma P. K. (2019). Evaluating the effect of codon optimization on expression of bar gene in transgenic tobacco plants. J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 28, 189–202. doi: 10.1007/s13562-019-00506-2 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

