Risk factors and treatment rationale for patellofemoral instability in the pediatric population
- PMID: 40433247
- PMCID: PMC12088301
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jposna.2024.100015
Risk factors and treatment rationale for patellofemoral instability in the pediatric population
Abstract
Patellofemoral instability (PFI) is one of the most common musculoskeletal problems in physically active children and young adults. PFI may significantly limit physical activity and increase the risk of developing arthritis long term. Identification and appropriate management of PFI is crucial in preventing long-term sequelae in the pediatric population. The purpose of this article is to review current concepts in PFI in young patients, focusing on epidemiology, risk factors, and treatment rationale.
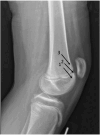
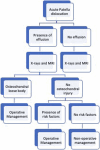
Key concepts: 1)Patella femoral instability (PFI) is most common in young, physically active female patients with predominance during adolescence between the ages of 13 and 18.2)Non-contact sports injuries are the most common mechanism of PFI injuries.3)Treatment of PFI involves non-operative and operative management with the goal of patellofemoral joint stability and high functionality.4)Surgical management is indicated for recurrent PFI. For first-time dislocation, selection of operative management depends on presence of risk factors for recurrent instability, such as trochlea dysplasia, patella alta, ligamentous laxity, and age as well as the presence of osteochondral injury.
Keywords: Children; Dislocation; Management; Patella; Recurrence.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
Nikolaos Paschos receives compensation from Arthroscopy Association of North America (AANA) for serving as an Associate Editor for the Arthroscopy Journal. All other authors report no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources