Differentiating Between Septic Arthritis and Lyme Arthritis in the Pediatric Population
- PMID: 40433346
- PMCID: PMC12088124
- DOI: 10.55275/JPOSNA-2023-706
Differentiating Between Septic Arthritis and Lyme Arthritis in the Pediatric Population
Abstract
Septic arthritis and Lyme arthritis are two conditions that can present with similar symptoms, making it challenging to differentiate between them in a clinical setting. While septic arthritis often requires immediate surgical intervention, Lyme arthritis can often be managed effectively with antibiotic therapy alone. However, given the dangerous nature of untreated septic arthritis, accurate diagnosis and timely intervention are crucial in managing the condition, especially in the pediatric population. Efforts to distinguish between the two conditions include the use of laboratory tests, history and physical exam findings, and MRI imaging. The authors aim to explore the causes, presentation, and treatment of septic versus Lyme arthritis as well as to provide a summary of the evolving research in this area and propose an algorithm that can aid in diagnosis. By synthesizing the proposed algorithm in diagnosis, clinicians will be better equipped to manage septic versus Lyme arthritis effectively while avoiding invasive procedures such as joint aspiration.
Key concepts: •Septic arthritis is a medical urgency that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment to achieve positive clinical outcomes.•Arthritis is a late-stage symptom of Lyme disease that can be challenging to distinguish from septic arthritis.•Laboratory tests, a thorough history & physical exam, and MRI imaging can aid in diagnosis and help clinicians manage these conditions without resorting to invasive procedures like arthrocentesis.•While septic arthritis usually requires joint drainage, Lyme arthritis can be managed effectively with antibiotic therapy.
© 2023 JPOSNA. Published by Elsevier on behalf of the Pediatric Orthopaedic Society of North America.
Figures
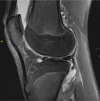
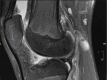
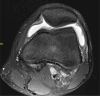
References
-
- Montgomery N.I., Epps H.R. Pediatric septic arthritis. Orthop Clin North Am. 2017;48(2):209–216. - PubMed
-
- Daikh B.E., Emerson F.E., Smith R.P., et al. Lyme arthritis: a comparison of presentation, synovial fluid analysis, and treatment course in children and adults. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2013;65(12):1986–1990. - PubMed
-
- Paakkonen M., Peltola H. Treatment of acute septic arthritis. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2013;32(6):684–685. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

