Tracing the history of clinical practice of liquid biopsy: a bibliometric analysis
- PMID: 40433362
- PMCID: PMC12105997
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1574736
Tracing the history of clinical practice of liquid biopsy: a bibliometric analysis
Abstract
Introduction: Liquid biopsy holds great promise in clinical diagnosis, treatment, and prognostic monitoring. This study reveals the development of liquid biopsy in clinical practice through a comprehensive bibliometric analysis.
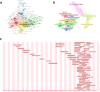
Methods: A total of 40 years of research literature in this field was included from the Web of Science Core Collection (WoSCC), analyzing the evolving research trends of liquid biopsy in clinical practice. We constructed co-occurrence networks for countries, institutions, authors, and keywords, integrating citation analysis and journal impact metrics to provide a comprehensive view of the research landscape in the field of liquid biopsy.
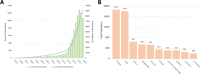
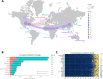
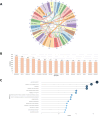
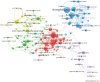
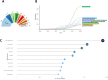
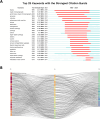
Results: The results show a significant growth trend in the clinical practice of liquid biopsy, with China and the United States being the leading contributors. Institutions such as Harvard University and the University of California system play a central role in the global collaboration network. Cancers has become the primary publication outlet for the field, while highly cited journals like Clinical Cancer Research play a crucial role in advancing its development. Keyword analysis reveals that research has progressively expanded into clinical applications, personalized treatment, and prognostic evaluation.
Discussion: Overall, as technology and applications continue to mature, liquid biopsy is expected to play an even greater role in the early diagnosis, treatment evaluation, and personalized treatment of cancer and other diseases.
Keywords: bibliometric analysis; biomarkers; cancer; clinical practice; liquid biopsy.
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Zhao, Wang, Li, Pan, Lu and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Research hotspots and frontiers of machine learning in renal medicine: a bibliometric and visual analysis from 2013 to 2024.Int Urol Nephrol. 2025 Mar;57(3):907-928. doi: 10.1007/s11255-024-04259-3. Epub 2024 Oct 30. Int Urol Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 39472403 Review.
-
Research Trends in the Application of Artificial Intelligence in Oncology: A Bibliometric and Network Visualization Study.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022 Aug 31;27(9):254. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2709254. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022. PMID: 36224012
-
Global scientific trends on thyroid disease in early 21st century: a bibliometric and visualized analysis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Jan 17;14:1306232. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1306232. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38298184 Free PMC article.
-
Current perspectives and trends of CD39-CD73-eAdo/A2aR research in tumor microenvironment: a bibliometric analysis.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 12;15:1427380. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1427380. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39188712 Free PMC article.
-
Global research trends and focus on immunotherapy for endometrial cancer: a comprehensive bibliometric insight and visualization analysis (2012-2024).Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 8;16:1571800. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1571800. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40264788 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

