A Bibliometric Analysis of Medication Compliance in Children with Asthma
- PMID: 40433421
- PMCID: PMC12109635
- DOI: 10.2147/JMDH.S514612
A Bibliometric Analysis of Medication Compliance in Children with Asthma
Abstract
Objective: Bibliometrics was used to visualize the literature data of the current study on medication compliance in children with asthma, which can provide reference for improving the medication compliance of children with asthma.
Methods: Using the bibliometrix package in R4.4.1, all the research literatures related to the medication compliance of children with asthma in the WOS core database were used, and the data visualization analysis of the retrieved research literatures was carried out.
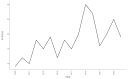
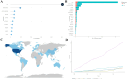
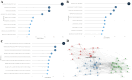
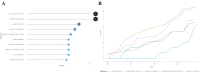
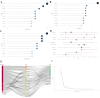
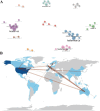
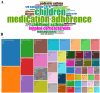
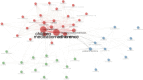
Results: A total of 285 research literatures on medication compliance in children with asthma were screened out. The earliest related research was published in 2009, and reaching its peak in 2019. The number of publications and citations related to medication compliance in children with asthma in the United States ranked first. J Allergy Clin Immun has 1043 citations in related journals. The analysis of cumulative publication volume shows that from 2009 to 2024, Journal of Asthma has the largest cumulative publication volume. Halterman Js is the most authoritative. The most frequently used keyword in these articles is "asthma". Statistical analysis of the high-frequency keywords in the literature on medication compliance in children with asthma showed that the top three high-frequency words were medication adherence, followed by unplanned children and childhood asthma.
Conclusion: The study on medication compliance in children with asthma was first published in 2009, and the research heat increased year by year. The most authoritative author in the field of medication compliance in children with asthma is Halterman Js. Journal of Asthma magazine is interested in the research field of medication compliance in children with asthma.
Keywords: asthma; bibliometrics; children; medication adherence.
© 2025 Zhao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
All of the authors had no any personal, financial, commercial, or academic conflicts of interest separately.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Evidence-Based Bibliometric Analysis of Acupuncture in Functional Dyspepsia: Clinical Efficacy and Research Trends.J Multidiscip Healthc. 2025 Apr 16;18:2141-2153. doi: 10.2147/JMDH.S515144. eCollection 2025. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2025. PMID: 40256110 Free PMC article.
-
Research progress of airway inflammation in asthma: A bibliometric analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Jul 19;103(29):e38842. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000038842. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39029036 Free PMC article.
-
Bibliometric analysis of global publications in medication adherence (1900-2017).Int J Pharm Pract. 2019 Apr;27(2):112-120. doi: 10.1111/ijpp.12471. Epub 2018 Jul 25. Int J Pharm Pract. 2019. PMID: 30044514
-
[A bibliometric analysis of research on occupational asthma during 1998 to 2017].Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 2019 Jun 20;37(6):425-431. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-9391.2019.06.005. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31256523 Chinese.
-
Research status and hotspots of medication safety in older adults: A bibliometric analysis.Front Public Health. 2023 Jan 5;10:967227. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.967227. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36684998 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

