The Influence of Implant Macro-geometry in Primary Stability in Low-Density Bone: An in vitro Study
- PMID: 40433430
- PMCID: PMC12105814
- DOI: 10.4103/jispcd.jispcd_155_24
The Influence of Implant Macro-geometry in Primary Stability in Low-Density Bone: An in vitro Study
Abstract
Aim: This study assessed the primary stability of implants featuring various geometries in polyurethane bone blocks simulating low-density bone types 3 and 4.
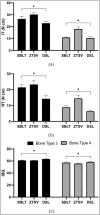
Methods: The study included 36 implants divided into three groups (Straumann BLT, n = 12; Zimmer TSV, n = 12; and Dentium Superline [DSL], n = 12). Implants featuring three different thread designs, a tapered body, a diameter of 4.0-4.1 mm, and a length of 10 mm were inserted into polyurethane bone blocks (20 and 15 PCF) to simulate bone types 3 and 4. Primary stability was evaluated using implant stability quotient (ISQ), insertion torque (IT), and removal torque (RT). IT and RT were compared using ANOVA, while ISQ was analyzed using the Kruskal-Wallis test. A P value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results: For bone type 3, the highest IT (30.21 ± 1.38 N cm) and RT (23.25 ± 2.30 N cm) value were observed for the Zimmer TSV, and the highest ISQ values (63.29 ± 0.54 N cm) were observed for DSL. For bone type 4, the highest IT (18.07 ± 1,71 Ncm) and RT (14.48 ± 1.81 Ncm) values were observed for the Zimmer TSV, and the highest ISQ values (58.46 ± 0.78 N cm) were observed for the DSL. The ISQ, IT, and RT values of the implant groups were significantly different (P < 0.001).
Conclusions: Implant geometry and bone density were key factors influencing primary stability in this study. The outcomes of the present study may help clinicians make decisions, especially when dealing with bone that has a less favorable quality. These findings may have important clinical implications related to immediate or early loading protocols, highlighting the critical role of implant design in attaining sufficient stability.
Keywords: Bone density; dental implant design; osseointegration; resonance frequency analysis (RFA).
Copyright: © 2025 Journal of International Society of Preventive and Community Dentistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Tumedei M, Piattelli A, Falco A, De Angelis F, Lorusso F, Di Carmine M, et al. An in vitro evaluation on polyurethane foam sheets of the insertion torque, removal torque values, and resonance frequency analysis (RFA) of a self-tapping threads and round apex implant. Cell Polym. 2021;40:20–30.
-
- Heitzer M, Kniha K, Katz MS, Winnand P, Peters F, Möhlhenrich SC, et al. The primary stability of two dental implant systems in low-density bone. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2022;51:1093–100. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources