Transcranial ultrasound stimulation in neuromodulation: a bibliometric analysis from 2004 to 2024
- PMID: 40433495
- PMCID: PMC12106416
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2025.1595061
Transcranial ultrasound stimulation in neuromodulation: a bibliometric analysis from 2004 to 2024
Abstract
Background: Transcranial ultrasound stimulation (TUS) is a non-invasive neuromodulation technique with promising clinical potential. Its therapeutic efficacy and safety are significantly influenced by stimulation parameters. However, the global research hotspots and future research trends of TUS application in the field of rehabilitation are unclear. This study analyzes the status of TUS research. Understand the annual publication trends, international and institutional cooperation pattern and influential authors and journals and keyword hotspot.
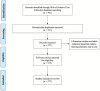
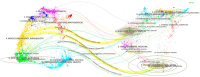
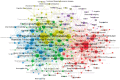
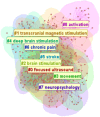
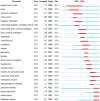
Methods: A comprehensive literature search was conducted on the Web of Science core database using TUS-related subject headings until 27 December 2024. Two researchers independently screened articles based on pre-determined inclusion and exclusion criteria. Software packages such as CiteSpace and VOSviewer were used to visualize the results.
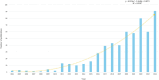
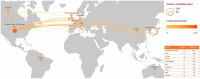
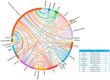
Results: A total of 577 literatures were included. The results show that the annual publication volume shows an increasing trend, reaching a peak in 2024. The United States, China and Germany dominated the number of publications, with the largest number of institutions being Harvard University, the University of Toronto and Brigham and Women's Hospital. Brain stimulation is the journal with the most articles and citations. Research hotspots include transcranial magnetic stimulation, noninvasive brain stimulation, Parkinson's disease, and Alzheimer's disease.
Conclusion: A bibliometric analysis of the literature shows that research interest in transcranial ultrasound stimulation is growing rapidly, with annual publications growing exponentially since 2013 and receiving increasing attention from researchers. The findings suggest that TUS is currently used primarily in neurological diseases, particularly in the study of Parkinson's disease and Alzheimer's disease. At the same time, it is found that an emerging international cooperation model with the partnership between the United States, China and Germany as the core has gradually taken shape. Although preclinical studies have shown promising neuromodulator effects, the current study suggests that TUS needs to undergo further multicenter clinical validation. These findings provide evidence to guide future research priorities for non-invasive neuromodulation.
Keywords: bibliometric analysis; neuromodulation; non-invasive brain stimulation; physiotherapy; transcranial ultrasound stimulation.
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Wang and Qie.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Blackmore D. G., Turpin F., Palliyaguru T., Evans H. T., Chicoteau A., Lee W., et al. (2021). Low-intensity ultrasound restores long-term potentiation and memory in senescent mice through pleiotropic mechanisms including NMDAR signaling. Mol. Psychiatry 26, 6975–6991. doi: 10.1038/s41380-021-01129-7, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bond A. E., Shah B. B., Huss D. S., Dallapiazza R. F., Warren A., Harrison M. B., et al. (2017). Safety and efficacy of focused ultrasound Thalamotomy for patients with medication-refractory, tremor-dominant Parkinson disease: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Neurol. 74, 1412–1418. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2017.3098, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

