Therapeutic Modulation of Demodex Density via Isotretinoin: Insights From a Prospective Dermatological Investigation
- PMID: 40433708
- PMCID: PMC12117431
- DOI: 10.1111/jocd.70249
Therapeutic Modulation of Demodex Density via Isotretinoin: Insights From a Prospective Dermatological Investigation
Abstract
Aim: Demodex spp. are ectoparasites that reside in pilosebaceous units, particularly on the face where sebum secretion is prominent. The sebum-reducing effects of isotretinoin play a crucial role in the management of acne vulgaris and rosacea. This study aims to assess the effect of isotretinoin on Demodex density in patients with acne vulgaris and rosacea accompanied by demodicosis. The evaluation includes Demodex mite density, before, during, and after 6 months of isotretinoin treatment.
Materials methods: The study included patients diagnosed with acne vulgaris and rosacea accompanied by demodicosis who were prescribed isotretinoin treatment. Demographic data were collected, and Demodex spp. mites were detected using superficial skin biopsy before treatment initiation. Follow-up samples were obtained at 2 and 6 months. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS version 23, with a significance level set at p < 0.05.
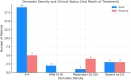
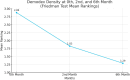
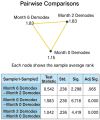
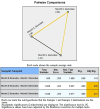
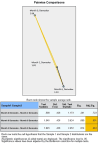
Results: A total of 36 patients, 25 with acne and 11 with rosacea, were included in our study. Demodex density was assessed before treatment, at 2 months, and at 6 months. Our findings showed a significant decrease in Demodex density with isotretinoin treatment, especially in relation to the decrease in sebum secretion (p < 0.001).
Conclusion: This study makes a notable contribution to the existing literature by being the first to assess the impact of isotretinoin treatment on Demodex density. Our results indicate that isotretinoin effectively reduces Demodex density, likely due to a reduction in sebum production. To further explore isotretinoin's effects, future research should involve larger sample sizes and extended follow-up periods. These findings enhance our understanding of isotretinoin's role in managing Demodex-related dermatological conditions.
Keywords: demodex; acne vulgaris; demodicosis; isotretinoin; rosace.
© 2025 The Author(s). Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Lee J. Y. and Hsu C. K., “Granulomatous Rosacea‐Like Demodicidosis,” Dermatology Online Journal 13, no. 4 (2007): 9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

