SCIG: Machine learning uncovers cell identity genes in single cells by genetic sequence codes
- PMID: 40433981
- PMCID: PMC12117433
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkaf431
SCIG: Machine learning uncovers cell identity genes in single cells by genetic sequence codes
Abstract
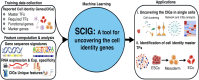
Deciphering cell identity genes is pivotal to understanding cell differentiation, development, and cell identity dysregulation involving diseases. Here, we introduce SCIG, a machine-learning method to uncover cell identity genes in single cells. In alignment with recent reports that cell identity genes (CIGs) are regulated with unique epigenetic signatures, we found CIGs exhibit distinctive genetic sequence signatures, e.g. unique enrichment patterns of cis-regulatory elements. Using these genetic sequence signatures, along with gene expression information from single-cell RNA-seq data, SCIG uncovers the identity genes of a cell without a need for comparison to other cells. CIG score defined by SCIG surpassed expression value in network analysis to reveal the master transcription factors (TFs) regulating cell identity. Applying SCIG to the human endothelial cell atlas revealed that the tissue microenvironment is a critical supplement to master TFs for cell identity refinement. SCIG is publicly available at https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.14726426 , offering a valuable tool for advancing cell differentiation, development, and regenerative medicine research.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures






References
-
- Davidson EH The Regulatory Genome: Gene Regulatory Networks in Development and Evolution. 2006; Academic Press; 10.1016/B978-0-12-088563-3.X5018-4. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01GM125632/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL133254/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM125632/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA278832/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL148338/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL148338/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA278832/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL155632/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM138407/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL133254/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01GM138407/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- Single Ventricle Research Foundation
- R01 HL155632/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

